Water knowledge
Understanding Water Purification Methods: A Comprehensive Guide to Safe Drinking Water
Understanding Water Purification Methods: A Comprehensive Guide to Safe Drinking Water. In today’s article, diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Common Water Purification Methods
Water purification is the process of removing impurities from water to make it safe for consumption. It’s crucial for safeguarding our health and well-being. There are various methods employed for this task, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Let’s explore the most common ones:
Physical Methods
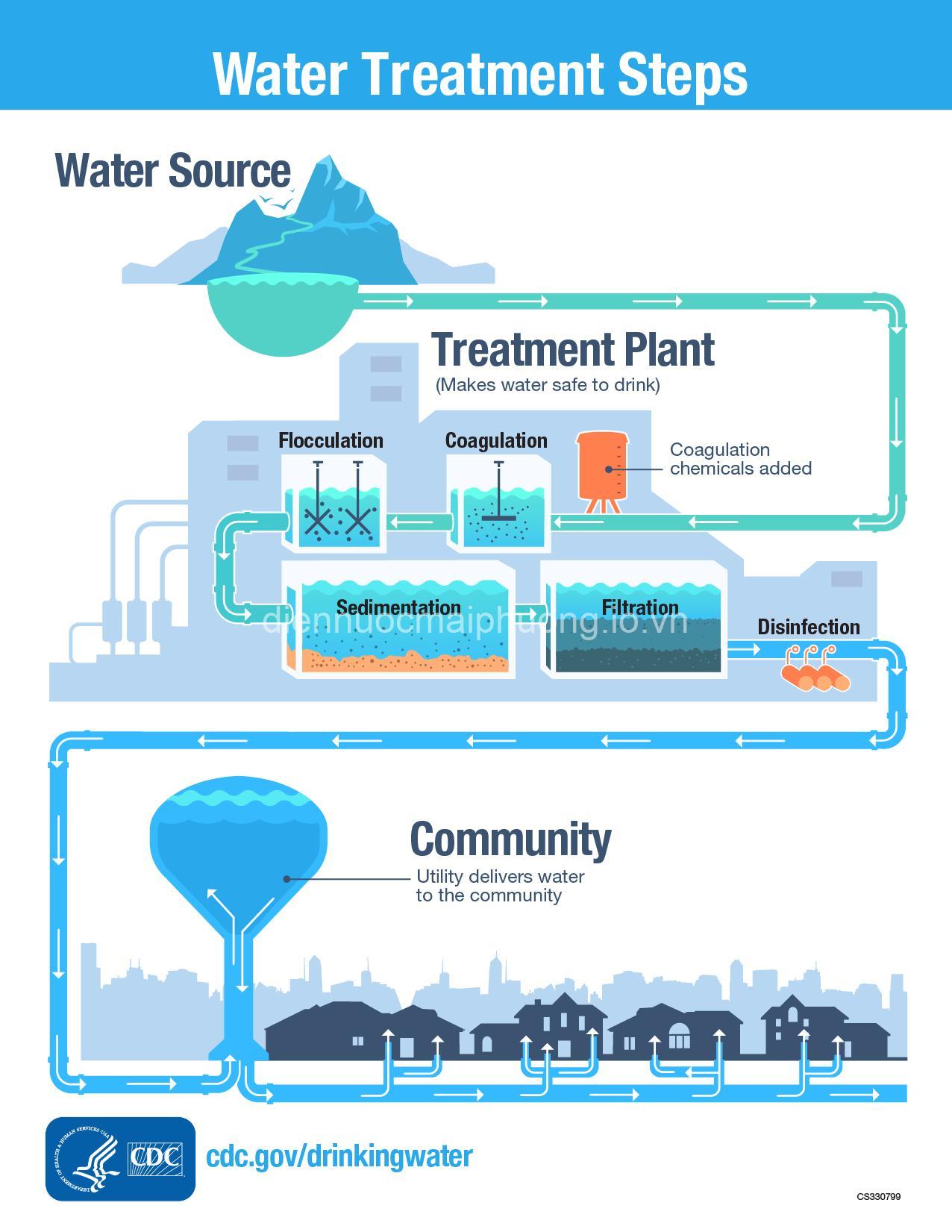
- Sedimentation: This simple method relies on gravity to settle heavier particles like sand, silt, and debris to the bottom of a container. While sedimentation effectively removes large particles, it doesn’t eliminate smaller contaminants.
- Filtration: This involves passing water through a porous barrier to trap impurities. There are several types of filters:
- Sand Filtration: This traditional method utilizes layers of sand and gravel to filter out suspended solids. Sand filters are often used in municipal water treatment plants.
- Membrane Filtration: This advanced technique uses semi-permeable membranes with microscopic pores to remove even smaller particles, including bacteria and viruses. Reverse osmosis (RO) and ultrafiltration (UF) are two popular membrane filtration methods.
- Carbon Filtration: This method employs activated carbon to adsorb organic compounds, chlorine, and other impurities from water. Carbon filters are commonly used in household water filters.
Chemical Methods
- Coagulation and Flocculation: These methods use chemicals to bind small particles together and form larger clumps (flocs) that can be easily removed by sedimentation or filtration. This is often used in municipal water treatment to remove suspended solids.
- Disinfection: This crucial step aims to kill harmful bacteria and viruses in water. Several methods are employed for disinfection:
- Chlorination: Chlorine is a powerful disinfectant that is commonly used in municipal water treatment plants. It effectively eliminates a wide range of pathogens but can leave a taste and odor in water.
- Ozonation: Ozone is a highly reactive gas that effectively disinfects water and removes organic compounds. It’s considered a more environmentally friendly alternative to chlorination.
- UV Radiation: Ultraviolet radiation can kill harmful bacteria and viruses in water by damaging their DNA. UV disinfection is often used for smaller water treatment systems.
- Boiling: Heating water to a rolling boil for one minute effectively kills most harmful bacteria and viruses. It’s a simple and reliable method, particularly for small quantities of water.
- Chemical Oxidation: This method uses oxidizing agents like chlorine or potassium permanganate to remove iron, manganese, and other contaminants. It is often used to improve the aesthetic quality of water by removing color and odor.
Biological Methods
- Biofiltration: This method utilizes a bed of media containing beneficial bacteria that feed on organic matter and other pollutants in water. Biofiltration is a natural and environmentally friendly way to purify water.
- Bioaugmentation: This technique involves introducing specific bacteria to enhance the biodegradation of pollutants in water. It is often used to remediate contaminated water sources.
Choosing the Right Water Purification Method
Selecting the best water purification method for your needs depends on several factors:
- Type and Concentration of Contaminants: The type and concentration of contaminants present in your water will determine the appropriate purification method. If your water contains high levels of bacteria, disinfection is essential. If you’re concerned about heavy metals, chemical oxidation may be necessary.
- Desired Quality of Purified Water: Consider the quality of water you desire. For drinking, you’ll likely need a higher quality of water than for general household use.
- Cost and Availability of Resources: The cost of different purification methods varies widely. Some methods, like boiling, are inexpensive and readily available. Others, like reverse osmosis, can be more costly.
- Environmental Impact: The environmental impact of different methods should be considered. Some methods, like chlorination, can generate byproducts that may be harmful to the environment. Others, like biofiltration, are more environmentally friendly.
Common Water Purification Systems
- Household Water Filters: These filters are designed for use in homes and provide a convenient way to purify tap water. There are various types of household filters, including pitcher filters, faucet filters, and whole-house filters.
- Municipal Water Treatment Plants: These large-scale facilities treat water for entire communities. They typically employ multiple purification methods, including sedimentation, filtration, coagulation, disinfection, and chemical oxidation.
- Portable Water Purifiers: These compact and portable devices are ideal for travel or emergency situations. They often use multiple methods, such as filtration, disinfection, and chemical oxidation, to purify water.
Water Purification Technologies: Innovations and Advancements
The field of water purification is constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging to address the growing global demand for safe drinking water.
- Nanomaterials in Water Purification: Nanomaterials have shown great potential in water purification. These materials have unique properties that can enhance filtration, disinfection, and contaminant removal processes. For example, nanofiltration membranes are being developed with higher efficiency and selectivity.
- Emerging Water Treatment Technologies: New water treatment technologies are being researched and developed, including:
- Membrane Distillation: This method utilizes a hydrophobic membrane to separate water from contaminants by evaporating and condensing water vapor.
- Electrocoagulation: This technology uses electrodes to generate coagulants and flocculants that remove contaminants from water.
- Advanced Oxidation Processes: These processes generate highly reactive species, such as hydroxyl radicals, to oxidize and degrade contaminants.
The Importance of Safe Drinking Water
Access to safe drinking water is fundamental to public health. Contaminated water can pose serious health risks, leading to waterborne diseases like cholera, typhoid fever, and dysentery. Long-term exposure to contaminants can also contribute to chronic health problems. It’s crucial to ensure that we have reliable and sustainable access to safe drinking water.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I know if my water is safe to drink?
- You can test your water for contaminants through a certified laboratory. Many home water testing kits are available, but these kits are typically less accurate than laboratory testing.
What are the most common water contaminants?
- Common water contaminants include bacteria, viruses, parasites, chemicals (like pesticides and herbicides), heavy metals (like lead and arsenic), and minerals (like calcium and magnesium).
How can I improve my water quality?
- You can install a whole-house water filter or use a water pitcher filter for drinking water. Additionally, consider using a faucet filter on your kitchen sink to improve the quality of water for cooking and drinking.
How often should I change my water filter?
- The recommended frequency for changing your filter depends on the type of filter and the water quality in your area. Check the manufacturer’s instructions for specific recommendations.
What are the latest advancements in water purification technology?
- Nanotechnology and advanced oxidation processes are some of the most promising advancements in water purification. These technologies offer efficient and sustainable solutions for water treatment.
Conclusion
Understanding water purification methods is crucial for ensuring access to safe drinking water. Choosing the right method depends on your specific needs and the contaminants present in your water. I hope this article has provided you with valuable information about water purification. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave a comment below! For more information on water purification systems and products, visit our website at diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn.
EAVs (Entity – Attribute – Value):
- Entity: Water | Attribute: Purity | Value: Safe, contaminated
- Entity: Water | Attribute: Source | Value: Tap water, well water, bottled water
- Entity: Water purification method | Attribute: Type | Value: Physical, chemical, biological
- Entity: Water purification method | Attribute: Effectiveness | Value: High, medium, low
- Entity: Water purification method | Attribute: Cost | Value: Expensive, affordable
- Entity: Water contaminant | Attribute: Type | Value: Bacteria, viruses, chemicals, minerals
- Entity: Water contaminant | Attribute: Source | Value: Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, sewage
- Entity: Water purification system | Attribute: Type | Value: Household filter, municipal treatment plant, portable purifier
- Entity: Water purification system | Attribute: Capacity | Value: Small, medium, large
- Entity: Water purification system | Attribute: Maintenance | Value: Easy, difficult
- Entity: Water quality | Attribute: Standard | Value: WHO guidelines, EPA regulations
- Entity: Water quality | Attribute: Testing | Value: Laboratory analysis, home test kits
- Entity: Water safety | Attribute: Risk | Value: High, medium, low
- Entity: Water health | Attribute: Impact | Value: Positive, negative
- Entity: Water resource management | Attribute: Goal | Value: Sustainability, conservation
- Entity: Water resource management | Attribute: Strategy | Value: Water harvesting, rainwater collection
- Entity: Water infrastructure | Attribute: Development | Value: Improved, outdated
- Entity: Water infrastructure | Attribute: Investment | Value: High, low
- Entity: Water pollution control | Attribute: Measures | Value: Wastewater treatment, pollution prevention
- Entity: Water pollution control | Attribute: Effectiveness | Value: Successful, limited
EREs (Entity, Relation, Entity):
- Entity: Water | Relation: Contains | Entity: Contaminants
- Entity: Water | Relation: Purified by | Entity: Water purification method
- Entity: Water purification method | Relation: Removes | Entity: Contaminants
- Entity: Water purification system | Relation: Uses | Entity: Water purification method
- Entity: Water contaminant | Relation: Impacts | Entity: Water quality
- Entity: Water contaminant | Relation: Affects | Entity: Human health
- Entity: Water quality | Relation: Determined by | Entity: Water purification process
- Entity: Water quality | Relation: Measured by | Entity: Water quality testing
- Entity: Water safety | Relation: Depends on | Entity: Water quality
- Entity: Water safety | Relation: Influenced by | Entity: Water purification system
- Entity: Water resource management | Relation: Aims to | Entity: Water sustainability
- Entity: Water resource management | Relation: Utilizes | Entity: Water conservation strategies
- Entity: Water pollution control | Relation: Prevents | Entity: Water contamination
- Entity: Water pollution control | Relation: Reduces | Entity: Water pollution
- Entity: Water infrastructure | Relation: Supports | Entity: Water treatment
- Entity: Water infrastructure | Relation: Influences | Entity: Water quality
- Entity: Water infrastructure | Relation: Requires | Entity: Investment
- Entity: Water health | Relation: Impacted by | Entity: Water quality
- Entity: Water health | Relation: Influences | Entity: Human health
- Entity: Public health | Relation: Linked to | Entity: Water safety
Semantic Triples (Subject, Predicate, Object):
- Subject: Water | Predicate: Is contaminated by | Object: Bacteria
- Subject: Water purification method | Predicate: Removes | Object: Viruses
- Subject: Water purification system | Predicate: Uses | Object: Filtration
- Subject: Filtration | Predicate: Removes | Object: Sediment
- Subject: Disinfection | Predicate: Kills | Object: Bacteria
- Subject: Water quality | Predicate: Is affected by | Object: Contaminants
- Subject: Water quality | Predicate: Is measured by | Object: Water quality testing
- Subject: Water safety | Predicate: Depends on | Object: Water quality
- Subject: Water safety | Predicate: Is improved by | Object: Water purification
- Subject: Water resource management | Predicate: Aims to | Object: Water sustainability
- Subject: Water pollution control | Predicate: Prevents | Object: Water contamination
- Subject: Water infrastructure | Predicate: Supports | Object: Water treatment
- Subject: Water health | Predicate: Is influenced by | Object: Water quality
- Subject: Public health | Predicate: Is impacted by | Object: Water safety
- Subject: Water | Predicate: Is essential for | Object: Human life
- Subject: Water purification | Predicate: Is a critical aspect of | Object: Public health
- Subject: Water contamination | Predicate: Can cause | Object: Waterborne diseases
- Subject: Water treatment | Predicate: Is used to | Object: Make water safe
- Subject: Water scarcity | Predicate: Is a major global challenge | Object: None
- Subject: Water conservation | Predicate: Is important for | Object: Sustainable water management
Semantic Keywords:
- Water treatment
- Water quality
- Drinking water
- Contamination
- Purification
- Filtration
- Disinfection
- Technology
- Sustainability
- Health
