Electrical Knowledge
Wire a Home Generator System: Step-by-Step Guide & Safety Tips
Wire a Home Generator System: Step-by-Step Guide & Safety Tips. In today’s article, diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Step-by-Step Guide to Wiring a Home Generator System
Before you start, remember that working with electricity can be dangerous. It’s essential to prioritize safety and follow all local electrical codes. If you’re unsure about any step, consult a licensed electrician. Now, let’s dive in!
Planning and Preparation
The first step is planning. You need to choose the right generator for your needs and select a suitable location for installation.
-
Choosing the Right Generator: The generator you choose should have enough power to run the essential appliances and systems in your home. Consider factors like:
- Power Output: Measured in kilowatts (kW), this determines how many appliances the generator can run simultaneously.
- Fuel Type: Common options include gas, diesel, and propane. Choose the fuel type that’s readily available and affordable in your area.
- Noise Level: Generators can be noisy, especially during operation. Consider the location and noise sensitivity of your neighbors when choosing.
- Runtime: This refers to how long the generator can run on a full tank of fuel. Look for a generator with a runtime that meets your needs in case of a prolonged power outage.
-
Selecting a Location: Find a level and stable surface for the generator. It should be easily accessible for refueling, maintenance, and ventilation. Ideally, choose a location:
- Close to a fuel source for convenient refueling.
- Well-ventilated to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
- Accessible to avoid tripping hazards.
-
Obtaining Permits: Check with your local building department for any permits required for generator installation.
-
Gathering Tools and Materials: You’ll need the following tools and materials:
- Wiring: Copper is the most common type of wire used for generator installations. The gauge (thickness) depends on the amperage required for your appliances.
- Connectors: Choose wire connectors compatible with the wiring you’re using.
- Circuit Breakers: Make sure to have the correct size and type of circuit breakers for your electrical panel and generator system.
- Safety Gear: Essential safety gear includes:
- Gloves: Wear insulated gloves to protect yourself from electrical shock.
- Eye protection: Safety glasses or goggles are crucial to shield your eyes from debris.
- Insulated Tools: Use insulated tools when working with electrical wiring to minimize the risk of shock.
Installing the Generator
Once you’ve planned and gathered the necessary materials, you can start installing the generator.
- Securing the Generator: Place the generator on a level surface and secure it to prevent it from moving during operation.
- Connecting the Fuel Source: Carefully connect the fuel lines from the generator to the fuel source (gas tank, propane tank, etc.) ensuring a tight and secure connection.
- Ensuring Proper Ventilation: The generator needs proper ventilation to avoid carbon monoxide buildup. Make sure the location has adequate airflow and is free of any obstructions.
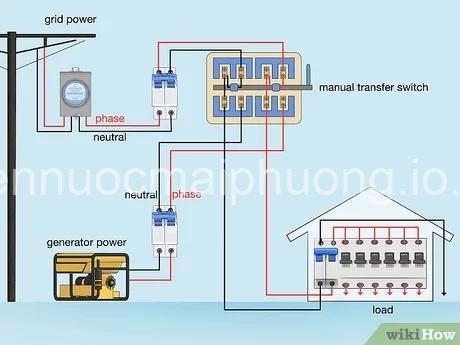
Installing the Transfer Switch
The transfer switch acts as a bridge between your home’s electrical system and the generator.
-
Choosing the Right Transfer Switch: Choose a transfer switch compatible with your generator’s power output and your home’s electrical system. Consider:
- Type: Transfer switches can be automatic or manual. Automatic switches automatically connect the generator to the electrical system when there’s a power outage, while manual switches require you to switch them manually.
- Size: The transfer switch needs to be large enough to handle the power output of your generator.
-
Selecting a Location: The transfer switch is usually installed in the electrical panel. If you’re planning to use it for certain circuits only, it may be installed elsewhere. However, it should be easily accessible.
- Wiring the Transfer Switch: Wiring the transfer switch involves connecting it to the generator and the main electrical panel. This process requires precise and accurate wiring to ensure proper operation.
Connecting the Generator to the Transfer Switch
Once you’ve installed the transfer switch, you can connect the generator to it.
- Identifying the Correct Wires: Identify the hot, neutral, and ground wires on both the generator and the transfer switch.
- Making Connections: Connect the generator’s wires to the transfer switch carefully, following wiring diagrams and electrical codes. Make sure the connections are tight and secure.
Testing and Troubleshooting
After you’ve completed the installation, it’s essential to test the system to ensure it’s working correctly.
- Starting the Generator and Testing the System: Start the generator and verify that it’s producing power. Check the electrical outlets and appliances connected to the generator to ensure they are receiving power.
- Troubleshooting Common Issues: If you encounter any problems, troubleshoot the system. Common issues include:
- No Power: Check the fuel level, the generator’s circuit breaker, and the transfer switch connections.
- Tripping Breakers: If the generator’s circuit breaker trips, it could indicate an overload or a short circuit.
- Consulting Manufacturer’s Instructions and Seeking Professional Help: If you’re unable to resolve any issues, consult the manufacturer’s instructions or contact a licensed electrician for assistance.
Essential Safety Precautions
Working with electricity requires utmost caution.
- Understanding the Risks of Working with Electricity: Electricity can be dangerous and even deadly. Always treat it with respect and take proper precautions.
- Using Proper Safety Gear: Wear gloves, eye protection, and insulated tools when working with electrical wiring to minimize the risk of injury.
- Disconnecting Power to the Main Breaker: Before working on any electrical system, always disconnect the power to the main breaker. This prevents accidental electrocution.
- Never Working on Live Wires: Never touch live wires with bare hands. Use insulated tools to make connections and avoid any direct contact.
- Seeking Professional Help When Necessary: If you’re unsure about any aspect of the installation or have any concerns, contact a licensed electrician.
Understanding the Components
To understand how a home generator system works, it’s essential to know the key components involved:
-
Generators:
- Portable Generators: These are smaller, more compact units that are typically used for temporary power needs.
- Standby Generators: These are larger, permanent installations designed to provide backup power for entire homes.
-
Transfer Switch: This is a crucial component that allows you to switch between the grid power and the generator power.
- Types: Transfer switches can be automatic or manual.
- Location: Transfer switches are typically installed in the electrical panel.
-
Wiring: The wiring used to connect the generator, transfer switch, and electrical panel needs to meet specific electrical codes.
- Types: The most common types of wiring are copper and aluminum.
- Gauge: The gauge of the wiring determines its capacity to carry current.
-
Circuit Breakers: Circuit breakers are essential safety devices that protect the electrical system from overloads and short circuits. They are usually located in the electrical panel.
Generator System Maintenance
To ensure your generator system operates smoothly and efficiently, regular maintenance is crucial.
-
Regular Maintenance Schedule: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for recommended maintenance intervals. This typically includes:
- Fuel Stabilizer: Use fuel stabilizer to prevent fuel degradation and ensure proper combustion.
- Oil Change: Change the oil regularly to prevent engine wear and tear.
- Cleaning: Clean the generator and transfer switch regularly to remove dirt and debris.
- Testing: Test the generator periodically to ensure it’s operating correctly.
-
Fuel Stability: Storing fuel for extended periods can lead to degradation and fuel problems. Use fuel stabilizer and store fuel in a properly sealed container.
- Safety Practices: Follow all safety instructions provided by the manufacturer when operating and maintaining the generator.
Choosing the Right Generator for Your Needs
Selecting the right generator is crucial for meeting your home’s power needs.
-
Factors to Consider:
- Power Output: Determine the total wattage needed to run the essential appliances and systems in your home.
- Fuel Type: Choose a fuel type readily available and affordable in your area.
- Noise Level: Consider the noise sensitivity of your neighbors and the location of the generator.
- Runtime: Choose a generator with a runtime that meets your needs during a power outage.
- Portability: Consider portability if you need a generator for temporary use.
-
Types of Generators:
- Standby Generators: These are typically installed permanently and automatically start when there’s a power outage.
- Portable Generators: These are smaller, more portable units that are suitable for temporary power needs.
-
Matching Generator Capacity to Your Home’s Power Needs: Calculate the total wattage of your appliances and systems to determine the generator’s required power output.
Benefits of a Home Generator System
Installing a home generator system offers several benefits:
- Peace of Mind During Power Outages: A generator provides peace of mind, knowing that your home will remain powered even during a power outage.
- Protecting Essential Appliances and Systems: You can protect essential appliances like refrigerators, furnaces, and medical equipment.
- Improving Home Comfort and Safety: Having power during an outage can make your home more comfortable and safe.
- Enhancing Resale Value: A generator system can increase the resale value of your home.
Additional Considerations
Beyond the basic installation, there are other important factors to consider:
- Local Electrical Codes and Regulations: Always follow local electrical codes and regulations when installing a generator system.
- Home Insurance Coverage: Check with your insurance provider to ensure your generator system is covered by your home insurance policy.
- Environmental Impact of Generator Emissions: Be mindful of the environmental impact of generator emissions and choose a generator with low emissions.
Conclusion
Wiring a home generator system requires careful planning, installation, and maintenance. By following the steps outlined above, you can install a reliable and safe system to power your home during outages. Remember to prioritize safety and seek professional help if needed.
For more information about electrical systems, generators, and other home improvement projects, visit diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn. We offer a wide range of high-quality electrical and plumbing products to meet your needs.
Don’t hesitate to share your thoughts, questions, or experiences by leaving a comment below. We also encourage you to share this article with your friends and family to help them prepare for power outages.
Jessica David Rodriguez
FAQs
How to determine the right size generator for your home?
To determine the right size generator, you need to calculate the total wattage of the appliances and systems you want to power during an outage. Add up the wattage of all appliances and systems you want to run simultaneously. Choose a generator with a power output that meets or exceeds that total wattage.
Can I install a home generator myself?
While it’s possible to install a home generator yourself, it’s generally recommended to have it installed by a licensed electrician, especially if you’re not comfortable working with electricity. Electricians have the expertise and knowledge to ensure the system is installed correctly and safely.
What type of transfer switch should I use?
Automatic transfer switches are generally preferred for home generator systems, as they automatically switch to generator power when the grid power goes out. Manual transfer switches require you to manually switch over to generator power, which can be inconvenient during a power outage.
What are some common generator troubleshooting tips?
Common troubleshooting tips for generators include:
- Check the fuel level: Make sure the generator has enough fuel to run.
- Inspect the circuit breaker: Ensure the generator’s circuit breaker is not tripped.
- Verify the transfer switch connections: Check that the transfer switch is properly connected to both the generator and the electrical panel.
- Check for overload: If the generator is overloaded, it may trip the circuit breaker. Try disconnecting some appliances or systems to reduce the load.
What maintenance tasks should I perform on my generator?
Regular maintenance tasks for generators include:
- Fuel stabilizer: Use fuel stabilizer to prevent fuel degradation, especially during storage.
- Oil change: Change the oil according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to prevent engine wear.
- Cleaning: Clean the generator’s exterior, air filter, and other parts regularly to remove dirt and debris.
- Testing: Run the generator periodically to ensure it’s operating correctly.
EAVs
- Generator – Type – Standby, Portable
- Generator – Fuel – Gas, Diesel, Propane
- Generator – Power Output – kW
- Transfer Switch – Type – Automatic, Manual
- Transfer Switch – Location – Electrical Panel
- Wiring – Type – Copper, Aluminum
- Wiring – Gauge – 10AWG, 12AWG
- Circuit Breaker – Amperage – 20A, 30A
- Electrical Panel – Size – 100 amp, 200 amp
- Safety Gear – Type – Gloves, Eye Protection, Insulated Tools
- Generator – Noise Level – dBA
- Generator – Runtime – Hours
- Generator – Warranty – Years
- Transfer Switch – Manufacturer – [Brand names]
- Wiring – Color – Black (hot), White (neutral), Green (ground)
- Circuit Breaker – Function – Overcurrent protection
- Electrical Panel – Manufacturer – [Brand names]
- Safety Gear – Manufacturer – [Brand names]
- Generator – Installation – Indoor, Outdoor
- Generator – Maintenance – Fuel stabilizer, Oil change
EREs
- Generator – Is Connected To – Transfer Switch
- Transfer Switch – Is Connected To – Electrical Panel
- Generator – Requires – Fuel Source
- Electrical Panel – Contains – Circuit Breakers
- Wiring – Connects – Generator, Transfer Switch, Electrical Panel
- Generator – Requires – Safety Gear
- Generator – Is Regulated By – Electrical Codes
- Home Improvement – Includes – Generator Installation
- Power Outage – Is Mitigated By – Generator System
- Generator – Uses – Fuel
- Generator – Produces – Power
- Circuit Breaker – Protects – Wiring
- Transfer Switch – Allows – Switching Between Grid Power and Generator Power
- Wiring – Is Subject To – Electrical Codes
- Electrical Panel – Provides – Access to Electrical System
- Safety Gear – Prevents – Electrical Shock
- Generator – Can Be – Portable or Standby
- Electrical System – Contains – Electrical Panel, Wiring, Circuit Breakers
- Transfer Switch – Can Be – Automatic or Manual
- Generator – Can Be – Powered by Gas, Diesel, or Propane
Semantic Triples
- (Generator, HasType, Standby)
- (Transfer Switch, IsLocatedIn, Electrical Panel)
- (Generator, Requires, Fuel Source)
- (Wiring, Connects, Generator)
- (Electrical Panel, Contains, Circuit Breakers)
- (Generator, Uses, Fuel)
- (Generator, Produces, Power)
- (Circuit Breaker, Protects, Wiring)
- (Transfer Switch, Allows, Switching Between Grid Power and Generator Power)
- (Generator, IsConnectedTo, Transfer Switch)
- (Transfer Switch, IsConnectedTo, Electrical Panel)
- (Generator, Requires, Safety Gear)
- (Generator, IsRegulatedBy, Electrical Codes)
- (Home Improvement, Includes, Generator Installation)
- (Power Outage, IsMitigatedBy, Generator System)
- (Generator, HasProperty, Noise Level)
- (Generator, HasProperty, Runtime)
- (Generator, HasProperty, Warranty)
- (Wiring, HasProperty, Gauge)
- (Wiring, HasProperty, Color)
