Electricity and Water News
Government Incentives for Renewable Energy Projects: Types, Benefits, and Challenges
Government Incentives for Renewable Energy Projects: Types, Benefits, and Challenges. In today’s article, diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Types of Government Incentives for Renewable Energy Projects
Governments worldwide recognize the importance of transitioning to renewable energy sources, and they employ a range of incentives to accelerate this shift. These incentives can be broadly categorized into three main types: financial incentives, regulatory incentives, and other incentives.
Financial Incentives offer direct financial support to renewable energy projects, making them more financially viable. Some common examples include:
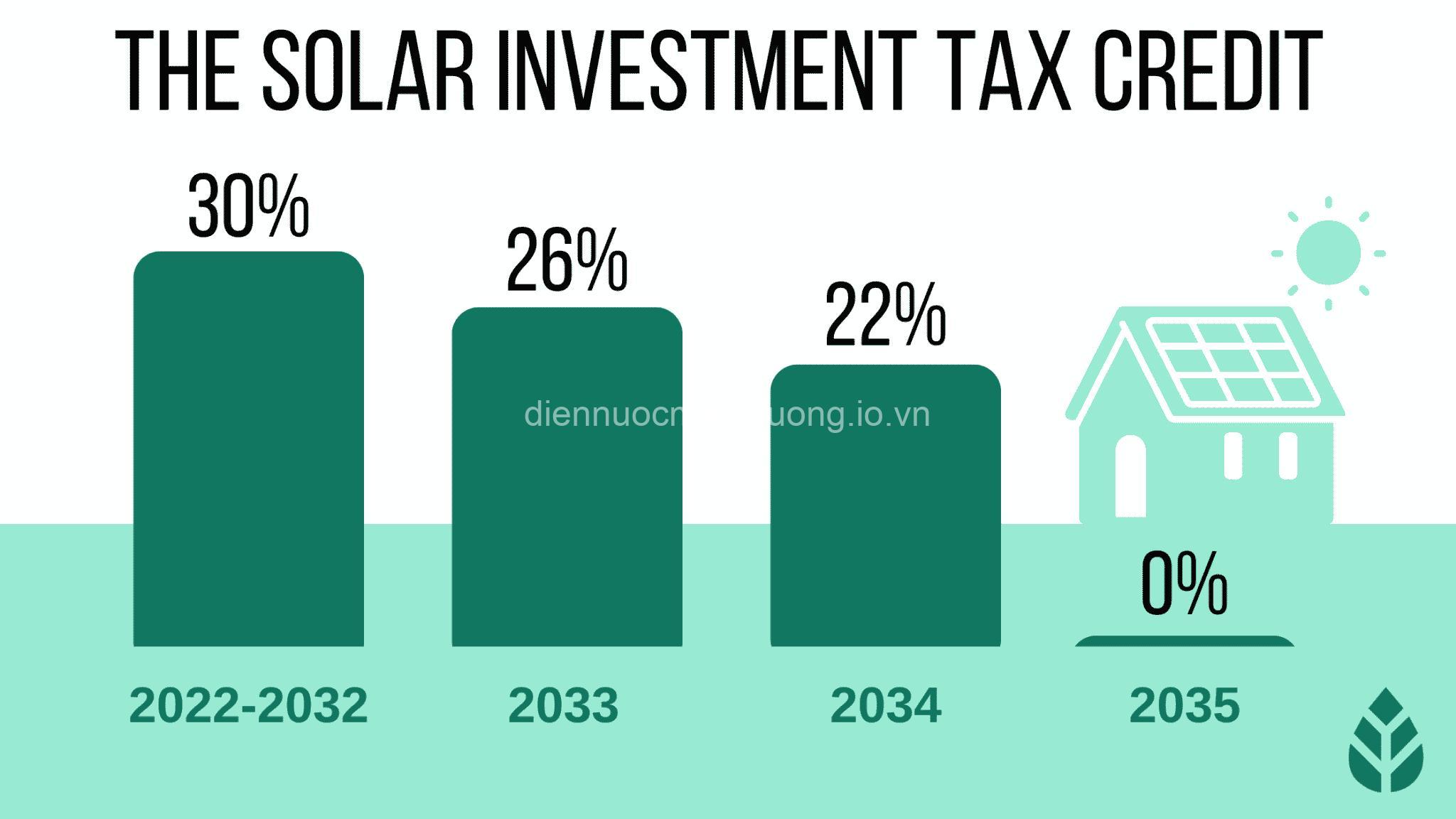
- Tax Credits: These are reductions in tax liability for individuals or businesses investing in renewable energy technologies. Investment tax credits provide tax breaks for the initial purchase of equipment, while production tax credits reward the generation of renewable energy.
- Grants: These are direct payments from government agencies to support renewable energy projects. Grants can be used for feasibility studies, construction, operation, and maintenance costs.
- Rebates: These offer a cash refund to consumers who invest in renewable energy technologies. Rebates can be offered on equipment purchases, installation costs, or energy savings.
- Loan Programs: Low-interest loans and loan guarantees can make renewable energy projects more affordable by reducing financing costs.
Regulatory Incentives create a favorable regulatory environment for renewable energy projects, encouraging their development and deployment. Some key examples include:
- Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS): These mandate that utilities generate a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources. RPS creates a guaranteed market for renewable energy, making it more attractive for investors.
- Feed-in Tariffs (FITs): These guarantee a fixed price for electricity generated from renewable sources for a specific period. FITs provide stability and long-term revenue certainty for renewable energy projects.
- Net Metering: This allows consumers who generate their own renewable energy to sell excess electricity back to the grid. Net metering incentivizes rooftop solar installations and encourages consumer participation in the energy transition.
- Streamlined Permitting Processes: Expediting the permitting process for renewable energy projects reduces delays and costs associated with project development.
Other Incentives play a vital role in creating a supportive environment for renewable energy projects. These can include:
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the benefits of renewable energy and promoting consumer demand.
- Research and Development Funding: Investing in research and development to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of renewable energy technologies.
Benefits of Government Incentives for Renewable Energy Projects
Government incentives play a crucial role in promoting renewable energy projects and reaping their numerous benefits. These benefits can be categorized into economic, environmental, and social advantages.
Economic Benefits:
- Job creation: The renewable energy sector creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research and development.
- Increased Investment: Incentives stimulate private investment in renewable energy infrastructure, leading to economic growth.
- Reduced Dependence on Fossil Fuels: Transitioning to renewable energy reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhancing national energy security.
Environmental Benefits:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, generate electricity without releasing greenhouse gases, combating climate change.
- Improved Air and Water Quality: Reduced fossil fuel consumption leads to cleaner air and water quality, improving public health.
- Increased Energy Security: By diversifying energy sources, renewable energy helps reduce reliance on volatile global energy markets, strengthening national energy security.
Social Benefits:
- Increased Energy Affordability: In the long term, renewable energy can reduce energy costs for consumers.
- Improved Public Health: Cleaner air and water quality resulting from reduced fossil fuel use lead to improved public health.
- Increased Energy Equity: Expanding access to renewable energy can benefit underserved communities and reduce energy disparities.
Challenges and Considerations for Government Incentives
While government incentives play a vital role in promoting renewable energy, they also present some challenges and considerations:
- Cost of Incentives: Providing incentives can impose a financial burden on taxpayers. Governments need to carefully balance the benefits of incentives with budget constraints.
- Equity Considerations: It is crucial to ensure that incentives are accessible to all communities, including underserved populations. Programs should be designed to avoid unintended consequences that might disproportionately impact marginalized communities.
- Effectiveness of Incentives: Evaluating the impact of different incentive programs is essential to ensure their effectiveness in promoting renewable energy deployment. Incentive design should be continually optimized for maximum impact.
Case Studies of Successful Government Incentive Programs
The effectiveness of government incentives is evident in numerous successful programs around the world. Here are a few notable examples:
- Germany’s Feed-in Tariff (FIT): Launched in 2000, the FIT played a significant role in boosting Germany’s renewable energy sector. It guaranteed a fixed price for electricity generated from renewable sources, making it a lucrative investment. The program’s success led to a dramatic increase in solar and wind energy production.
- California’s Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS): California’s RPS requires utilities to generate a specific percentage of their electricity from renewable sources. The program has been instrumental in driving the state’s transition to renewable energy, attracting significant private investment and creating jobs.
- The United States Investment Tax Credit (ITC): The ITC provides tax credits for investments in renewable energy technologies. The credit has been extended and enhanced several times, demonstrating the government’s commitment to supporting the renewable energy sector. The ITC has incentivized significant investment in solar and wind energy, contributing to their growth.
Future Trends in Government Incentives for Renewable Energy Projects
As the renewable energy sector continues to evolve, government incentives are likely to adapt and evolve as well. Some key future trends include:
- Emerging Technologies: Incentives are expected to focus on emerging renewable energy technologies, such as offshore wind, solar energy storage, and green hydrogen production. These technologies have the potential to significantly expand the renewable energy sector.
- Market Dynamics: Incentive programs will likely adapt to the changing market dynamics in the renewable energy sector. This includes addressing challenges related to grid integration, storage capacity, and intermittency of renewable energy sources.
- International Cooperation: International cooperation is becoming increasingly important for scaling up renewable energy deployment. This includes exploring global carbon pricing mechanisms and renewable energy trade agreements to promote cross-border collaboration.
FAQs
What is the main purpose of government incentives for renewable energy projects?
The main purpose of government incentives is to encourage the development and deployment of renewable energy projects by making them more financially attractive and reducing the risks associated with investing in these technologies.
How do government incentives affect the cost of renewable energy?
Government incentives can significantly reduce the cost of renewable energy by providing financial support, reducing financing costs, and creating a more favorable regulatory environment.
What are some common examples of government incentives?
Common examples of government incentives include tax credits, grants, rebates, feed-in tariffs, renewable portfolio standards, and net metering.
What are the potential risks associated with government incentives?
Potential risks associated with government incentives include the cost to taxpayers, the potential for unintended consequences, and the need to ensure that incentives are effective and equitable.
What are some future trends in government incentives for renewable energy?
Future trends in government incentives include a focus on emerging technologies, adaptations to changing market dynamics, and increased international cooperation.
Conclusion
Understanding government incentives for renewable energy projects is essential for anyone interested in investing in a sustainable future. These incentives play a critical role in promoting the development and deployment of clean energy technologies, ultimately contributing to a greener and more sustainable planet.
For more insights into renewable energy and sustainable living, be sure to visit my website at https://diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn. Share your thoughts and experiences with government incentives in the comments section below.
– Jessica David Rodriguez
