Electrical Knowledge
Basic Electrical Wiring for Homes: Understanding the Basics & Key Components
Basic Electrical Wiring for Homes: Understanding the Basics & Key Components. In today’s article, diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding the Basics of Electrical Wiring
Before we dive into the specifics of wiring, let’s grasp the core concepts. Electrical wiring is essentially the system of wires that carry electricity throughout your home, powering everything from lights and appliances to outlets and switches.
Imagine electricity as a river flowing through a network of pipes. The voltage represents the pressure pushing the water (electricity) through the pipes, while the current represents the amount of water (electricity) flowing through. Finally, resistance is like friction in the pipes, slowing down the flow of water. These three elements are interconnected, and their interaction is described by Ohm’s Law, a fundamental principle in electronics.
In your home, you deal with alternating current (AC), which continuously changes direction. This is unlike direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. AC is the standard for homes because it’s easier to transmit over long distances, making it efficient for our power grid.
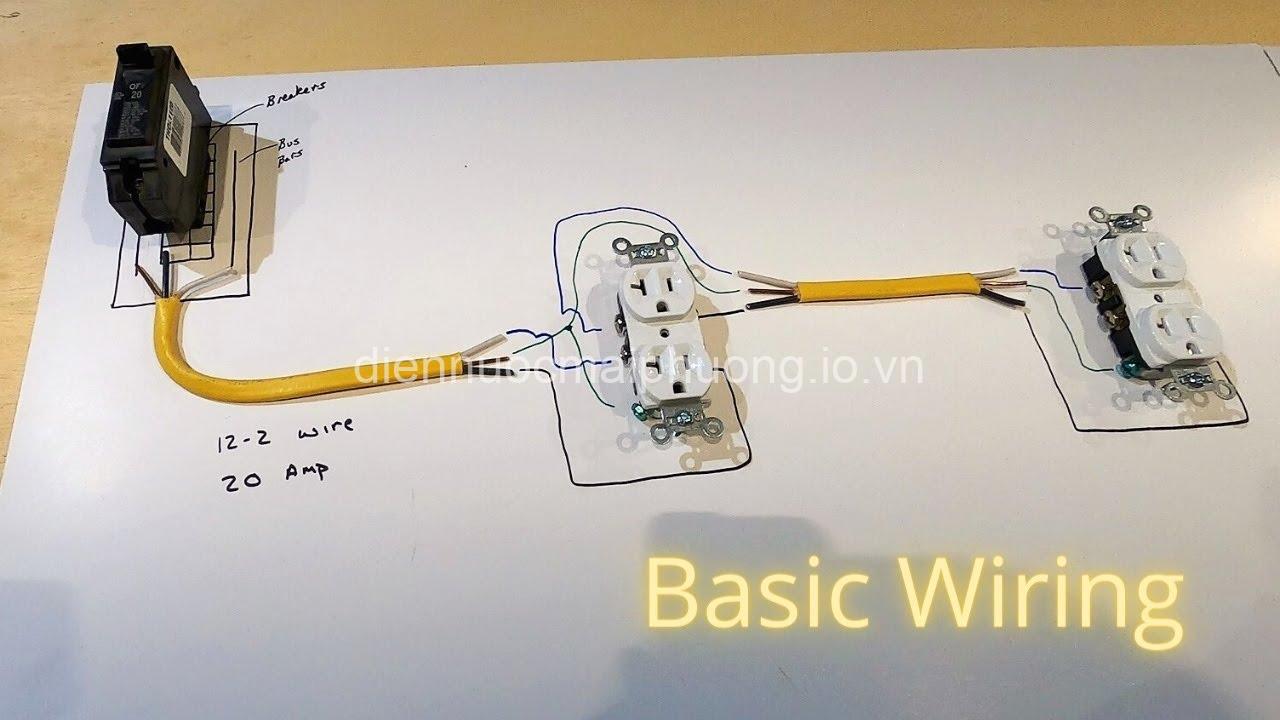
Key Components of a Home’s Electrical System
Now, let’s explore the key elements of a home’s electrical system:
The Electrical Panel (Breaker Box)
The electrical panel is the central hub of your home’s electrical system, acting like the control center for the entire network. It’s where the main power line enters your house and gets distributed to different circuits throughout your home. Inside the panel, you’ll find a series of circuit breakers, which act as safety switches, automatically interrupting the flow of electricity to a particular circuit in case of an overload or short circuit, preventing electrical fires or damage.
Types of Electrical Wiring
The wires themselves are the pathways for electricity, and there are various types commonly used in homes. Romex and NM-B cable are popular choices for residential wiring. They contain insulated conductors that carry electricity, along with a bare grounding wire that protects against electrical shock by providing a path for stray electricity to safely flow to the earth.
Outlets and Switches
Outlets provide the connection points for your appliances and devices, while switches allow you to control the flow of electricity to specific circuits. There are different types of outlets, like GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets, which are particularly important in areas like bathrooms and kitchens because they protect against electrical shock caused by ground faults. AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets, on the other hand, help prevent electrical fires caused by arcing faults.
Electrical Fixtures
Electrical fixtures, like light fixtures, ceiling fans, and appliances, are the devices that consume electricity. It’s crucial to ensure these fixtures are correctly wired and installed by a qualified electrician to prevent safety hazards.
Understanding Electrical Circuits
Types of Circuits
Circuits are the pathways through which electricity flows, starting at the electrical panel and reaching various outlets and fixtures. A series circuit has only one path for electricity to flow, while a parallel circuit has multiple paths. In homes, parallel circuits are preferred because they allow appliances to function independently, meaning that if one appliance stops working, others on the same circuit will remain operational.
Circuit Breakers and Fuses
As mentioned earlier, circuit breakers are safety devices that automatically break the circuit if there’s an overload or short circuit. They are designed to protect the wiring and prevent electrical fires. Fuses serve a similar purpose but are designed to burn out and break the circuit when an overload occurs. While circuit breakers are now more common, you might still find fuses in older homes.
Safety First: Electrical Wiring Precautions
Electricity can be dangerous, so it’s crucial to handle electrical wiring with utmost care and respect. DIY electrical work is often discouraged, as it can lead to dangerous situations and costly damage. Always prioritize safety and hire a qualified electrician for complex or potentially hazardous electrical projects.
Importance of Professional Electricians
Qualified electricians possess the knowledge, skills, and experience to handle electrical wiring safely and efficiently. They are familiar with electrical codes and regulations, ensuring that your electrical system is installed and maintained correctly. They are also equipped with the appropriate tools and safety gear, minimizing risks and potential hazards.
General Safety Tips
Here are some general safety tips to remember when working around electricity:
- Always turn off the power to the circuit before working on it. Use a voltage tester to confirm the power is off before proceeding.
- Wear gloves and eye protection to protect yourself from electrical shock and potential debris.
- Avoid working on electrical wiring when wet, as water can conduct electricity.
- Be cautious when working with electrical wiring and avoid touching exposed wires.
- Inspect electrical wiring regularly for signs of damage or wear.
- If you suspect a potential electrical problem, contact a qualified electrician immediately.
Additional Resources and Information
If you want to delve deeper into electrical wiring and learn more about the topic, there are numerous resources available:
- Websites: Many websites offer comprehensive information on electrical wiring, including helpful guides, tutorials, and safety tips.
- Books: There are numerous books available covering electrical wiring, ranging from beginner guides to more advanced technical manuals.
- Organizations: Electrical code authorities and organizations like the National Electrical Code (NEC) provide valuable resources and guidelines for safe electrical practices.
Troubleshooting Common Electrical Issues
While electrical problems can be intimidating, some basic troubleshooting can be helpful for minor issues.
Identifying Common Problems
Here are some common signs of potential electrical problems:
- Flickering lights: Could indicate a loose connection, faulty bulb, or overloaded circuit.
- Tripping breakers: Indicates a problem with the circuit, such as an overload or short circuit.
- Burnt outlets: Indicates a potential wiring issue or a faulty device.
- Shocking sensations: A clear sign of a potential ground fault and requires immediate attention from a professional.
Simple Fixes You Can Do
You can handle some basic electrical issues, but always ensure the power is off before doing so:
- Replacing a burnt-out lightbulb: A simple task that involves unscrewing the old bulb and screwing in a new one.
- Resetting a tripped breaker: Locate the tripped breaker in the electrical panel and switch it back to the “on” position.
When to Call a Professional
For any more complex electrical issues, don’t hesitate to call a licensed electrician. Here are some scenarios where a professional is crucial:
- Repeated tripping of breakers: Could indicate a serious problem that requires expert attention.
- Burning smells or visible sparks: Clear signs of an electrical issue that should be addressed immediately by a professional.
- Wiring damage: If you see any damage to wiring, including loose connections, frayed wires, or burned insulation, call a qualified electrician right away.
- Any doubts: If you are unsure about handling an electrical issue, it’s always best to err on the side of caution and contact a professional electrician.
FAQs about Basic Electrical Wiring for Homes
What are the different types of wires used in residential wiring?
There are many types of wires used in residential wiring, including:
- Romex: A common type of cable with insulated conductors and a grounding wire.
- NM-B cable: Similar to Romex, it’s widely used for residential wiring.
- THHN: A flexible wire that is often used for connections in electrical panels.
What is the purpose of grounding wires?
Grounding wires provide a path for stray electricity to safely flow to the earth, reducing the risk of electrical shock. They are crucial for electrical safety.
What is the difference between a circuit breaker and a fuse?
Both circuit breakers and fuses protect electrical systems from overloads. Circuit breakers can be reset, while fuses are designed to burn out and need to be replaced after an overload.
What is the difference between a GFCI and an AFCI?
GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets protect against electrical shock caused by ground faults. AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets protect against electrical fires caused by arcing faults.
What are some common electrical issues that homeowners should be aware of?
Common electrical issues include:
- Flickering lights
- Tripping breakers
- Burnt outlets
- Shocking sensations
- Burning smells or visible sparks
- Wiring damage
Conclusion
Understanding the basics of electrical wiring is crucial for every homeowner. By learning about the different components, safety precautions, and common issues, you can ensure a safe and efficient electrical system in your home. For any complex electrical tasks, remember to consult a qualified electrician for professional assistance. To learn more about electricity, water, and related products, visit our website at https://diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn/. Let us know your thoughts and questions in the comments section below, and share this article with others who might find it useful!
Jessica David Rodriguez, owner of Diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn, has been providing high-quality electrical and plumbing products and services for over 10 years. Her mission is to empower homeowners with knowledge about electricity and water systems.
EAV:
1. Electrical wiring – Type – Romex
2. Electrical wiring – Type – NM-B cable
3. Electrical panel – Function – Distribute power
4. Circuit breaker – Function – Protect circuit from overloads
5. Grounding wire – Purpose – Safety
6. Outlet – Type – GFCI
7. Outlet – Function – Provide power to appliances
8. Switch – Type – Toggle switch
9. Switch – Function – Control electrical flow
10. Wire nut – Function – Connect wires
11. Electrical code – Purpose – Ensure safe electrical installations
12. Electrician – Role – Install and repair electrical systems
13. Electrical shock – Hazard – Injury or death
14. Overloaded circuit – Hazard – Fire risk
15. Faulty wiring – Hazard – Electrical shock, fire risk
16. DIY electrical work – Risk – Injury, electrical damage
17. Electrical inspection – Purpose – Ensure safety of electrical system
18. Home electrical system – Components – Panel, wiring, outlets, switches
19. Electrical wiring – Installation – Follow code requirements
20. Electrical wiring – Maintenance – Regular inspection and repair
ERE:
1. Home – Has – Electrical system
2. Electrical system – Contains – Wiring
3. Electrical system – Contains – Panel
4. Electrical system – Contains – Outlets
5. Electrical system – Contains – Switches
6. Circuit – Flows through – Wires
7. Outlet – Connected to – Circuit
8. Switch – Controls – Circuit
9. Electrician – Installs – Electrical system
10. Electrician – Repairs – Electrical system
11. Electrical code – Regulates – Electrical installations
12. Grounding wire – Connects – Ground
13. Circuit breaker – Protects – Circuit
14. GFCI – Protects – User from shock
15. AFCI – Protects – Against arc faults
16. Wire nut – Connects – Wires
17. Electrical shock – Caused by – Faulty wiring
18. Electrical fire – Caused by – Overloaded circuit
19. Homeowner – Needs to – Understand electrical safety
20. DIY electrical work – Requires – Caution and knowledge
Semantic Triple:
1. (Electrical wiring, is, component of home electrical system)
2. (Circuit, flows through, wires)
3. (Outlet, provides, power)
4. (Switch, controls, electrical flow)
5. (Grounding wire, ensures, safety)
6. (Electrical code, defines, safe installation practices)
7. (Electrician, installs and repairs, electrical systems)
8. (DIY electrical work, can be, dangerous)
9. (Electrical inspection, verifies, safety of electrical system)
10. (Homeowner, should understand, basic electrical concepts)
11. (Electrical shock, can cause, injury or death)
12. (Overloaded circuit, can lead to, electrical fire)
13. (Faulty wiring, poses, electrical hazards)
14. (Electrical panel, distributes, power)
15. (Circuit breaker, protects, against overloads)
16. (Romex, is a type of, electrical wiring)
17. (NM-B cable, is a type of, electrical wiring)
18. (GFCI, protects against, electrical shock)
19. (AFCI, protects against, arc faults)
20. (Wire nut, connects, wires securely)
