Electrical Knowledge
Electrical Transformers: How They Work & Their Types
Electrical Transformers: How They Work & Their Types. In today’s article, diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
How Transformers Work: The Fundamentals of Electromagnetic Induction
Transformers are essential components in our electrical systems, playing a crucial role in transmitting and distributing electricity. But have you ever wondered how these devices actually work? It all comes down to the fundamental principle of electromagnetic induction.
Imagine a magnet moving near a coil of wire. This movement creates a changing magnetic field, which in turn induces an electric current in the coil. This is the essence of electromagnetic induction, the foundation upon which transformers operate.
Faraday’s Law:
Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction is the bedrock of transformer function. It states that the magnitude of the induced electromotive force (EMF) in a coil is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux passing through the coil. This means that the faster the magnetic field changes, the greater the voltage induced in the coil.
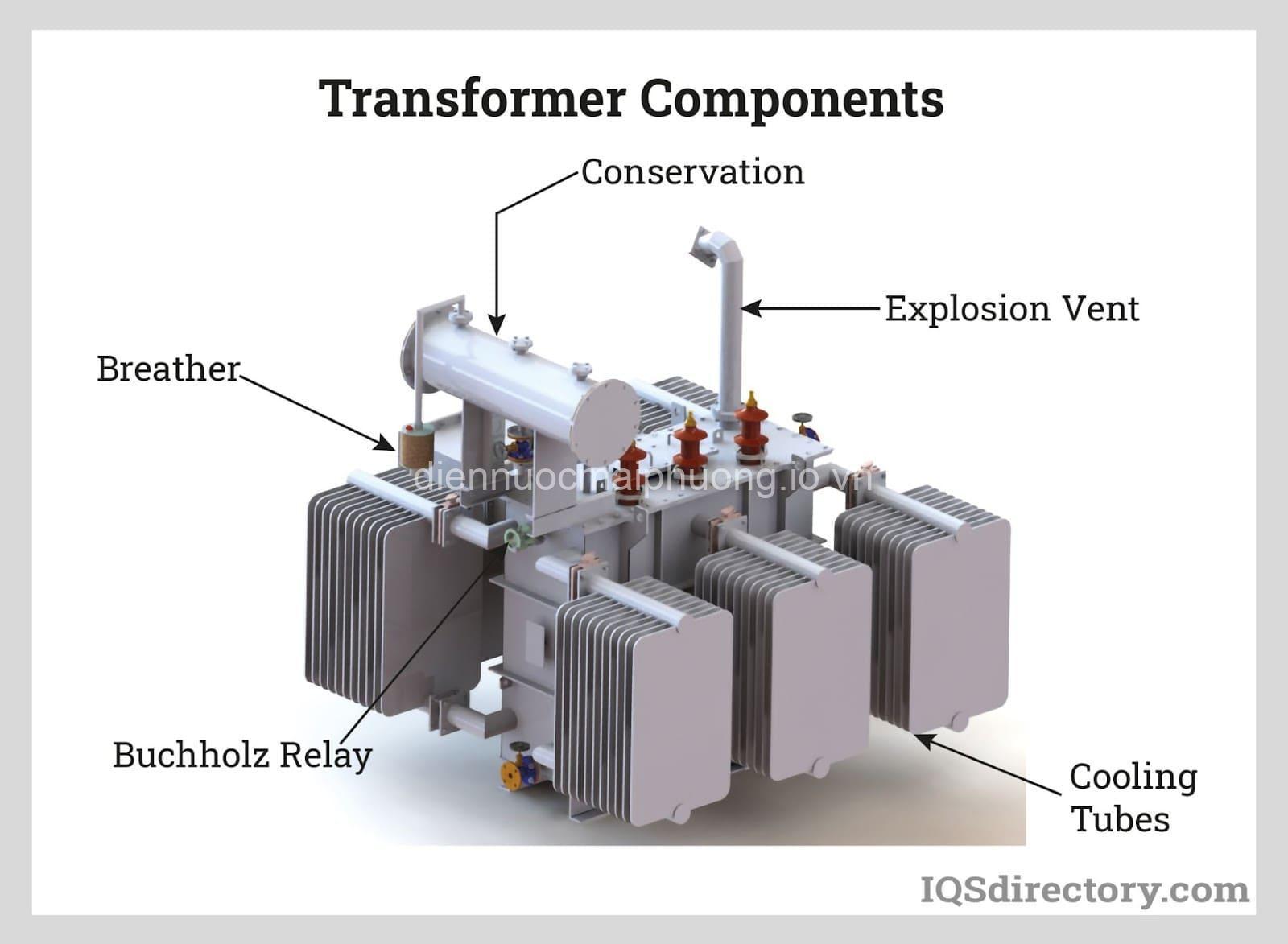
Transformer Components:
A transformer consists of two main components: windings and a core.
-
Windings: These are coils of wire wrapped around the core. There are two windings: the primary winding and the secondary winding. The primary winding is connected to the source of alternating current (AC), while the secondary winding is connected to the load.
-
Core: The core is made of a ferromagnetic material, like iron or laminated steel, which helps to concentrate the magnetic field created by the windings.
Working Principle:
When AC current flows through the primary winding, it creates a changing magnetic field that passes through the core. This changing magnetic field then induces an EMF in the secondary winding. The voltage induced in the secondary winding is proportional to the number of turns in the secondary winding compared to the number of turns in the primary winding. This ratio is known as the turns ratio.
Turns Ratio:
The turns ratio is crucial in determining the voltage transformation of a transformer. If the secondary winding has more turns than the primary winding, the transformer is a step-up transformer, increasing the voltage. Conversely, if the secondary winding has fewer turns than the primary winding, the transformer is a step-down transformer, decreasing the voltage.
Types of Transformers: Step-Up, Step-Down, and More
Transformers come in different forms, each designed for specific purposes. Here are some common types:
-
Step-up Transformers: These transformers increase voltage and decrease current. Think of them as “voltage boosters.” They’re vital for transmitting electricity over long distances. Increasing the voltage reduces current, which minimizes energy loss during transmission.
-
Step-down Transformers: These transformers decrease voltage and increase current. Imagine them as “voltage reducers.” They are essential in bringing high-voltage electricity from the power grid to our homes and businesses.
-
Autotransformers: These transformers have only one winding that serves as both the primary and secondary winding. They can either step-up or step-down voltage but are not as widely used as traditional step-up or step-down transformers.
-
Other Types: In addition to step-up, step-down, and autotransformers, there are other specialized transformers like isolation transformers and current transformers. Isolation transformers are used to prevent electrical shock by separating circuits from ground, while current transformers are used to measure current in high-voltage circuits.
Applications of Transformers: Powering Our World
Transformers are essential components in our modern world. Let’s explore their diverse applications:
-
Power Transmission: Transformers play a crucial role in long-distance power transmission. They enable the efficient transmission of electricity by stepping up the voltage to reduce power loss. Imagine a power plant generating electricity, and that power needs to reach a city hundreds of miles away. The high voltage generated by the power plant is further increased using step-up transformers, minimizing power loss during transmission.
-
Electrical Devices: Transformers are found in countless electrical devices, from power supplies to chargers for our smartphones and laptops. These devices use transformers to convert the high voltage from the power grid into the lower voltage required for safe operation.
-
Industrial and Other Applications: Transformers are also essential in various industrial processes, such as welding, where they supply high current at lower voltages, and medical equipment where they are used to power specialized medical devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Transformers
Transformers offer numerous advantages, but they also have some drawbacks. Here’s a quick breakdown:
Advantages:
- Increased Efficiency in Power Transmission: Transformers are highly efficient, minimizing energy loss during power transmission.
- Voltage Regulation and Safety: Transformers help maintain a stable voltage level, ensuring safe operation of electrical systems.
- Flexibility in Power Distribution: Transformers allow for flexible power distribution by enabling different voltage levels.
Disadvantages:
- Cost and Size Limitations: Transformers can be expensive and bulky, especially for high-power applications.
- Potential Noise and Magnetic Field Issues: Transformers can generate noise and magnetic fields, which can be a concern in certain applications.
The Importance of Transformers in Our Modern World
In conclusion, transformers are indispensable components of our electrical infrastructure, facilitating the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity. From powering our homes to operating essential industrial equipment, transformers are the backbone of our modern world.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further innovation in transformer design, perhaps leading to even more efficient and compact transformers in the future.
For more information about electrical transformers and other essential components, I encourage you to visit my website at https://diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn.
Please feel free to leave a comment, share this post with your friends, or explore other interesting topics on my website. Together, let’s delve deeper into the fascinating world of electricity and plumbing!
What are the main components of a transformer?
Answer: The main components of a transformer are the primary winding, the secondary winding, and the core. The primary winding is connected to the source of alternating current (AC), while the secondary winding is connected to the load. The core, made of a ferromagnetic material, helps to concentrate the magnetic field created by the windings.
What is a turns ratio, and how does it affect the voltage transformation?
Answer: The turns ratio is the ratio of the number of turns in the secondary winding to the number of turns in the primary winding. This ratio determines the voltage transformation of the transformer. If the secondary winding has more turns than the primary winding, the transformer is a step-up transformer, increasing the voltage. Conversely, if the secondary winding has fewer turns than the primary winding, the transformer is a step-down transformer, decreasing the voltage.
What is the difference between a step-up transformer and a step-down transformer?
Answer: A step-up transformer increases the voltage and decreases the current, while a step-down transformer decreases the voltage and increases the current. Step-up transformers are used in power transmission, while step-down transformers are used to bring high-voltage electricity to homes and businesses.
What are some applications of transformers in industrial settings?
Answer: Transformers are used in numerous industrial applications, including welding, where they supply high current at lower voltages, and manufacturing, where they are used to power large machinery. They also play a role in powering specialized equipment in various industries, such as those related to food processing, chemical production, and metalworking.
What are the main advantages of using transformers in electrical systems?
Answer: The main advantages of using transformers in electrical systems include increased efficiency in power transmission, voltage regulation and safety, and flexibility in power distribution. Transformers help minimize energy loss during power transmission, ensure safe operation of electrical systems by maintaining stable voltage levels, and allow for flexible power distribution by enabling different voltage levels.
