Electricity and Water News
Electricity Export Agreements: Benefits, Challenges & Key Considerations
Electricity Export Agreements: Benefits, Challenges & Key Considerations. In today’s article, diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
The Growing Need for Regional Energy Cooperation
The need for regional energy cooperation has become more apparent in recent years. As countries strive to meet their growing energy needs, they’re realizing the importance of diversifying their energy sources and reducing their dependence on single suppliers. Regional energy collaboration offers a solution, allowing countries to share resources, leverage economies of scale, and build a more resilient energy infrastructure.
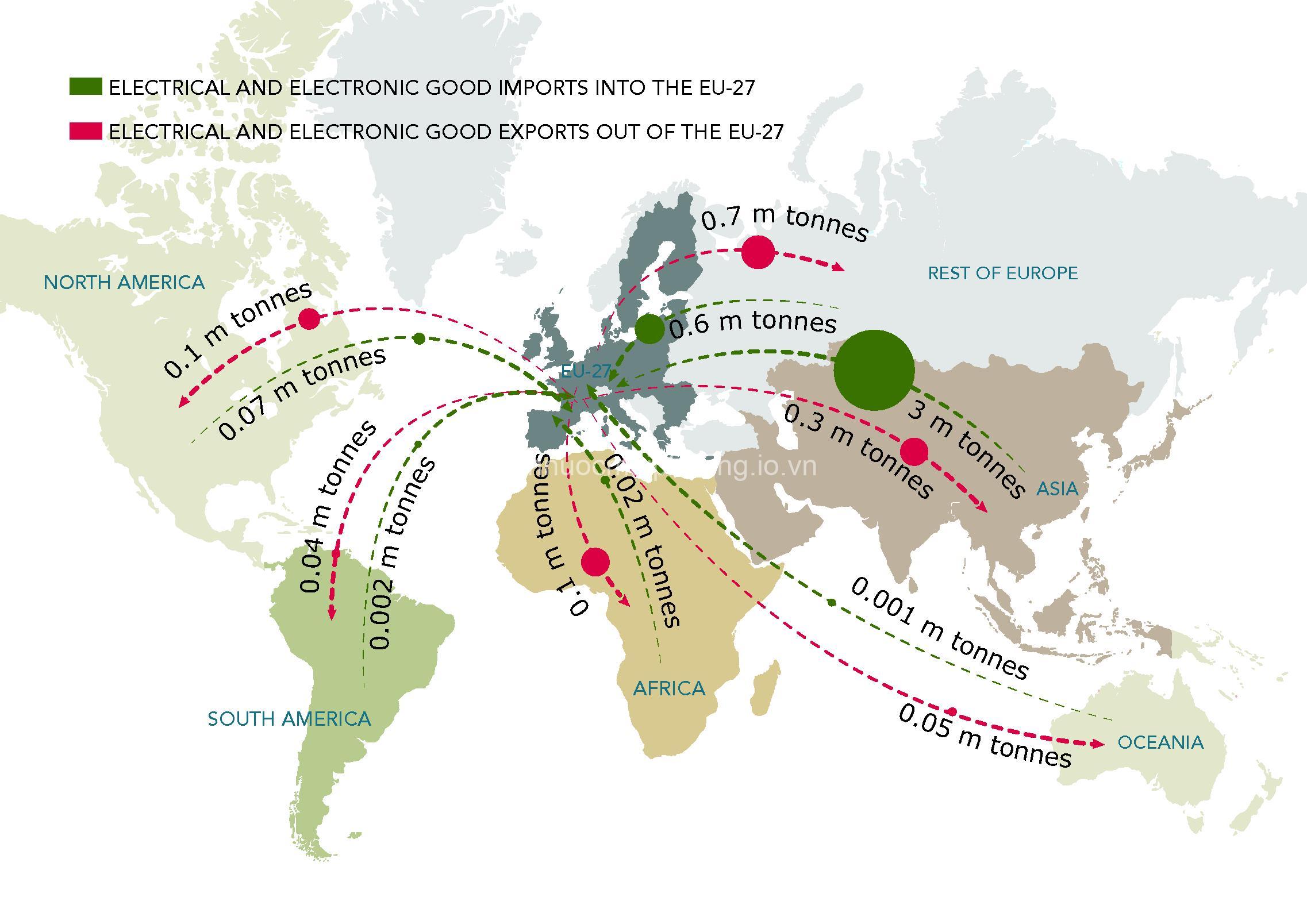
What are Electricity Export Agreements?
Electricity export agreements are legal frameworks that govern the cross-border trade of electricity between neighboring countries. These agreements define the terms of trade, including the volume of electricity to be exchanged, pricing mechanisms, and the responsibilities of each party.
There are several types of electricity export agreements:
- Bilateral agreements: These agreements involve two countries and focus on specific energy needs and market dynamics.
- Multilateral agreements: These agreements involve multiple countries and often encompass larger regional energy markets. They aim to facilitate large-scale energy exchange and promote regional integration.
- Hybrid agreements: These agreements combine elements of both bilateral and multilateral arrangements, offering a tailored approach to meet specific needs.
Benefits of Electricity Export Agreements
Electricity export agreements offer significant benefits for participating countries:
- Enhanced Energy Security: By diversifying energy sources and reducing reliance on single suppliers, these agreements strengthen energy security. They create a more resilient energy system, minimizing the impact of disruptions or crises.
- Economic Development: Electricity export agreements stimulate economic growth by facilitating trade, attracting investment, and creating jobs in related industries.
- Promotion of Regional Integration: By fostering collaboration and interdependence, these agreements promote regional integration and strengthen political ties between participating countries.
- Sustainable Development: Electricity export agreements can facilitate the integration of renewable energy resources, promoting a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
Challenges of Electricity Export Agreements
While these agreements hold considerable promise, they also present several challenges:
- Technical Challenges: Synchronizing grids across borders, ensuring interoperability, and building the necessary transmission infrastructure require significant technical expertise and investment.
- Economic Challenges: Determining fair pricing mechanisms, managing investment costs, and ensuring a level playing field in the market are crucial considerations.
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: Harmonizing technical standards, negotiating contracts, and establishing effective dispute resolution mechanisms are essential for a smooth and reliable energy trade.
- Political and Geopolitical Challenges: Political instability, conflicting interests, and a lack of trust can hinder the implementation and effectiveness of these agreements.
Key Considerations in Electricity Export Agreements
When establishing and implementing electricity export agreements, several crucial considerations come into play:
Technical Considerations:
- Grid Synchronization and Interoperability: This ensures the seamless flow of electricity across borders. It involves coordinating the frequency and voltage of interconnected grids, ensuring their compatibility for efficient power transfer.
- Transmission Infrastructure Development: Investing in power lines, substations, and other infrastructure is crucial to transport electricity efficiently and reliably across borders.
- Harmonization of Technical Standards: Ensuring that the equipment and operating procedures used in each country are compatible is essential for a smooth and reliable flow of electricity.
Economic Considerations:
- Pricing Mechanisms and Tariffs: Determining fair and transparent pricing structures for electricity traded across borders is crucial for attracting investors and ensuring long-term sustainability.
- Investment Costs and Return on Investment: Securing funding for infrastructure development and ensuring an attractive return on investment are key considerations for investors.
- Market Competition and Regulatory Frameworks: Establishing competitive and fair market conditions for electricity trading is essential to ensure efficient resource allocation and foster sustainable energy development.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations:
- Contractual Obligations and Dispute Resolution: Negotiating clear and comprehensive agreements that outline the rights and responsibilities of each party, along with effective dispute resolution mechanisms, is crucial for a smooth and predictable energy trade.
- Environmental and Social Impact Assessments: Conducting thorough assessments to minimize the negative environmental and social impacts of energy projects and promote sustainable development is a key aspect of responsible energy cooperation.
- Energy Security Considerations and Risk Management: Addressing potential vulnerabilities and mitigating risks associated with cross-border electricity trade is essential for ensuring energy security and resilience.
Examples of Successful Electricity Export Agreements
Several successful electricity export agreements serve as models for regional energy cooperation. Here are some notable examples:
- ASEAN Power Grid: This initiative aims to create an interconnected power grid across Southeast Asia, facilitating cross-border electricity trade and promoting regional energy integration.
- Southern African Power Pool: This organization coordinates electricity trade among member countries in Southern Africa, enabling them to share resources, manage power fluctuations, and improve energy security.
These successful examples highlight the benefits of collaborative planning, strong political will, and efficient infrastructure development in promoting regional energy cooperation. They demonstrate the potential for electricity export agreements to contribute to economic growth, energy security, and sustainable development.
Challenges and Opportunities in Electricity Export Agreements
While electricity export agreements offer immense potential, they also face numerous challenges and opportunities.
Challenges:
- Political Instability and Geopolitical Tensions: Political instability and geopolitical tensions can hinder the implementation and effectiveness of electricity export agreements. These factors can create uncertainty, disrupt cross-border collaboration, and undermine the long-term sustainability of energy projects.
- Lack of Coordination and Transparency: A lack of coordination and transparency among stakeholders can lead to delays, disputes, and inefficiencies. Effective communication, clear roles and responsibilities, and open data sharing are essential for successful implementation.
- Environmental and Social Concerns: Energy projects often raise environmental and social concerns, requiring careful planning, mitigation strategies, and stakeholder engagement to minimize negative impacts and promote sustainable development.
- Financial Constraints and Investment Risks: Securing funding for large-scale energy projects can be challenging, particularly in developing countries. Managing investment risks, such as political instability and regulatory changes, is crucial for attracting investors.
Opportunities:
- Advancements in Energy Storage Technologies: Advances in energy storage technologies, such as battery storage and pumped hydro, offer new opportunities for enhancing grid flexibility and integrating renewable energy resources.
- Growing Demand for Renewable Energy: The increasing demand for renewable energy presents opportunities for cross-border trade in clean energy, promoting sustainable development and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Increased Focus on Regional Integration and Cooperation: A growing awareness of the benefits of regional energy cooperation is encouraging countries to work together to address energy challenges and build a more resilient energy future.
- Technological Advancements in Grid Management and Interconnectivity: Advancements in grid management systems and smart grid technologies are improving the efficiency and reliability of electricity transmission, enabling more complex cross-border energy exchange.
The Future of Electricity Export Agreements
The future of electricity export agreements is promising, with advancements in technology and a growing global focus on sustainable energy. We can expect:
- Increased Regional Energy Integration: More countries are likely to engage in regional energy cooperation, forming interconnected electricity markets that promote efficient resource allocation, reduce energy costs, and foster sustainable development.
- Enhanced Role of Renewable Energy: Cross-border trade in renewable energy is expected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing demand for clean and sustainable energy sources.
- Technological Advancements: Further advancements in grid management, energy storage, and smart grid technologies will facilitate more complex and efficient cross-border electricity trade.
- Policy and Regulatory Reforms: Policy and regulatory reforms are crucial for fostering a supportive environment for electricity export agreements. These reforms should address challenges related to infrastructure development, market access, and investment promotion.
Conclusion
Electricity export agreements play a crucial role in promoting regional energy security, economic development, and sustainable development. As countries work together to meet their growing energy needs, these agreements offer a powerful tool for building a more interconnected, resilient, and sustainable energy future.
To learn more about the electrical and plumbing products and services offered by Jessica David Rodriguez and diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn, visit our website at: https://diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn.
We encourage you to leave a comment below, share this article with your network, and explore more informative content on our website.
FAQs about Electricity Export Agreements with Neighboring Countries
What are the main drivers of electricity export agreements?
The primary drivers of electricity export agreements include:
- Increased demand for reliable and affordable electricity: Driven by population growth, urbanization, and industrial development, countries are seeking reliable and affordable electricity supply.
- Regional energy cooperation and integration: Countries are recognizing the benefits of sharing resources, promoting energy efficiency, and fostering economic growth through regional collaboration.
- Political and diplomatic considerations: These agreements can strengthen bilateral relations, address regional energy challenges collaboratively, and contribute to broader political and diplomatic goals.
What are the key considerations in negotiating electricity export agreements?
Negotiating electricity export agreements requires careful consideration of several factors, including:
- Technical aspects: Ensuring grid synchronization, interoperability, and adequate transmission infrastructure is crucial for a smooth flow of electricity.
- Economic aspects: Establishing fair pricing mechanisms, attracting investments, and managing market competition are essential for the economic viability of these agreements.
- Legal and regulatory aspects: Harmonizing technical standards, negotiating contracts, and establishing dispute resolution mechanisms are crucial for a stable and predictable energy trade.
What are some examples of successful electricity export agreements?
Examples of successful electricity export agreements include:
- ASEAN Power Grid: This initiative facilitates cross-border electricity trade among Southeast Asian nations, promoting regional energy integration.
- Southern African Power Pool: This organization coordinates electricity trade among Southern African countries, fostering regional cooperation and improving energy security.
What are the main challenges facing electricity export agreements?
Challenges facing electricity export agreements include:
- Political instability and geopolitical tensions: These factors can create uncertainty and hinder cross-border collaboration.
- Lack of coordination and transparency: Effective communication and collaboration among stakeholders are essential for successful implementation.
- Environmental and social concerns: Minimizing negative environmental and social impacts and promoting sustainable development is crucial.
- Financial constraints and investment risks: Securing funding and managing investment risks associated with large-scale energy projects can be challenging.
What are the opportunities for the future of electricity export agreements?
Opportunities for the future include:
- Advancements in energy storage technologies: New energy storage technologies can enhance grid flexibility and integrate renewable energy.
- Growing demand for renewable energy: Cross-border trade in clean energy is expected to grow.
- Increased focus on regional integration and cooperation: A growing awareness of the benefits of regional energy cooperation encourages collaboration.
- Technological advancements in grid management and interconnectivity: Advancements in grid technologies improve the efficiency and reliability of electricity transmission.
EAVs:
- Agreement – Type – Power Purchase Agreement (PPA)
- Agreement – Signatories – Country A, Country B
- Agreement – Duration – 10 years
- Power grid – Capacity – 1000 MW
- Power grid – Interoperability – Yes/No
- Country – Energy consumption – 100 TWh/year
- Country – Renewable energy share – 20%
- Investment – Amount – $1 billion
- Investment – Source – Private sector
- Infrastructure – Type – Transmission lines
- Infrastructure – Length – 100 km
- Energy security – Level – High/Medium/Low
- Economic development – Impact – Positive/Negative
- Environmental impact – Type – Carbon emissions reduction
- Regulatory framework – Type – National/Regional
- Power grid – Ownership – Public/Private
- Agreement – Dispute resolution mechanism – Arbitration
- Country – Political stability – Stable/Unstable
- Investment – Return on investment – 10%
- Agreement – Objective – Energy security, economic development
ERE:
- Country – exports – Electricity
- Agreement – regulates – Electricity trade
- Power grid – connects – Countries
- Investment – supports – Infrastructure development
- Infrastructure – facilitates – Electricity transmission
- Agreement – aims to enhance – Energy security
- Electricity trade – impacts – Economic development
- Renewable energy – contributes to – Sustainable development
- Country – implements – Energy policy
- Agreement – establishes – Regulatory framework
- Country – has – Power grid
- Power grid – has – Capacity
- Agreement – involves – Investment
- Investment – comes from – Private sector
- Country – faces – Challenges
- Challenges – affect – Agreement implementation
- Country – has – Energy consumption
- Agreement – contributes to – Regional integration
- Agreement – includes – Environmental safeguards
- Electricity export – impacts – Environmental impact
Semantic Triples:
- Country A – exports – Electricity to Country B
- Power Purchase Agreement – regulates – Electricity trade between Country A and Country B
- Power grid – connects – Country A and Country B
- Investment – supports – Construction of transmission lines
- Transmission lines – facilitates – Electricity transmission from Country A to Country B
- Agreement – aims to enhance – Energy security in Country B
- Electricity trade – impacts – Economic growth in Country B
- Renewable energy sources – contribute to – Sustainable development in Country A
- Country A – implements – National energy policy
- Agreement – establishes – Regional regulatory framework
- Country A – has – National power grid
- National power grid – has – Limited transmission capacity
- Agreement – involves – Foreign direct investment
- Foreign direct investment – comes from – Private sector companies
- Country B – faces – Political instability
- Political instability – affects – Agreement implementation
- Country B – has – High energy consumption
- Agreement – contributes to – Regional energy integration
- Agreement – includes – Environmental impact assessment
- Electricity export – impacts – Carbon emissions
