Electricity and Water News
Electricity Supply Challenges in Developing Regions: Crucial Role & Barriers
Electricity Supply Challenges in Developing Regions: Crucial Role & Barriers. In today’s article, diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
The Crucial Role of Electricity Access for Development
Imagine a world where lighting up your home, powering your business, or even accessing clean water relies on unreliable electricity. Sadly, this reality is faced by millions in developing regions. Electricity access isn’t just a luxury; it’s a crucial driver of economic growth, social progress, and sustainable development.
Think about it. Electricity fuels industries, creating jobs and boosting productivity. Reliable electricity empowers businesses to thrive, attracting investments and creating opportunities for local communities. But limited electricity access can hinder economic growth, trapping communities in a cycle of poverty.
Beyond economics, electricity access also plays a vital role in social progress. It enables healthcare facilities to operate effectively, bringing life-saving treatments to underserved communities. Schools can utilize technology, enhancing education and opening up opportunities for future generations. And basic amenities like clean water and sanitation become more accessible with reliable power.
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) recognize the importance of electricity access as a key factor in achieving sustainable development. The goal of providing affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all by 2030 highlights the crucial role of electricity in building a brighter future.
It’s important to remember that sustainable development involves balancing economic growth with environmental protection. While electricity is essential for progress, relying solely on fossil fuels can lead to air pollution, climate change, and unsustainable practices. This is why investing in renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower is crucial for a sustainable future.
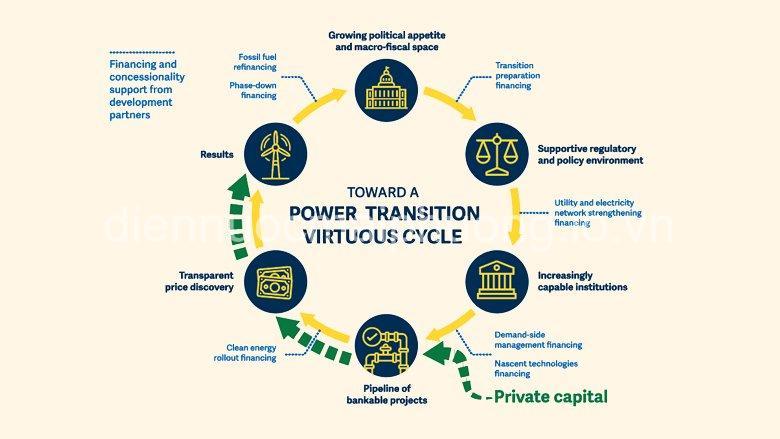
Key Challenges to Electricity Supply in Developing Regions
While the benefits of electricity are undeniable, developing regions face significant challenges in providing reliable and sufficient power. Here are some of the key obstacles:
-
Limited Grid Infrastructure: In many developing regions, particularly in rural areas, the electricity grid infrastructure is limited and underdeveloped. This restricts access to electricity for large segments of the population, particularly those living in remote communities. Developing a robust grid network requires significant investment in transmission lines, distribution networks, and other essential infrastructure.
-
Outdated Technology: Many developing countries rely on aging and inefficient power generation systems, often relying heavily on fossil fuels. These systems contribute to high energy costs, environmental pollution, and unreliable electricity supply. Upgrading outdated technology with modern and more efficient systems is critical.
-
Lack of Investment in Renewable Energy: Despite the potential of renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower to provide clean and sustainable power, investment in these technologies remains limited in many developing regions. This is due to a variety of factors, including high upfront costs, technical complexities, and inadequate policy support.
Economic and Financial Barriers to Electrification
Beyond infrastructure and technology, economic and financial barriers can significantly hinder electrification efforts in developing regions.
-
Poverty and Limited Resources: For many developing countries, poverty and limited resources make it challenging to invest in large-scale electrification projects. Limited access to financial markets further restricts the ability to secure funding for these projects.
-
Debt Burden and Access to Capital: Many developing countries face high levels of debt, which can make it difficult to secure loans and attract foreign investment for electrification projects. Limited access to international capital markets adds another hurdle, making it challenging to obtain the necessary financial resources.
-
High Energy Costs: Inefficient infrastructure and lack of competition can lead to high energy costs, making it difficult for individuals and businesses to afford electricity. This can stifle economic activity, further exacerbating the cycle of poverty.
Political and Social Factors Impeding Electricity Access
Beyond economic constraints, political and social factors can also pose significant challenges to electrification efforts.
-
Political Instability and Corruption: Political instability can create an environment of uncertainty, deterring investors and making it difficult to implement long-term electrification projects. Corruption can lead to inefficient resource allocation, diverting funds from essential infrastructure development.
-
Lack of Government Support and Policy Frameworks: Strong government policies, clear regulations, and effective institutions are crucial for encouraging private sector investment, promoting renewable energy development, and ensuring sustainable electrification strategies. Lack of government support and ineffective policy frameworks can create an unfavorable environment for electrification efforts.
-
Limited Access to Education and Training: A skilled workforce is essential for operating and maintaining power infrastructure. However, limited access to education and training programs in many developing countries can create a shortage of qualified personnel in the electricity sector. This can lead to inefficiencies and difficulties in managing electrification projects.
The Impact of Limited Electricity Access
The consequences of limited electricity access are far-reaching and can significantly impede development.
-
Hindered Economic Growth: Businesses struggling to operate due to unreliable electricity supply may struggle to grow and create jobs. Industrial development is also hampered, limiting diversification of economies and hindering economic growth.
-
Health and Education Challenges: Healthcare facilities relying on generators for power may experience frequent disruptions, jeopardizing the delivery of essential services. Schools without electricity face limited access to technology, impacting the quality of education and limiting opportunities for students.
-
Environmental Concerns: Many developing countries heavily rely on fossil fuels to generate electricity. This leads to air pollution, contributing to respiratory illnesses and other health problems. Furthermore, the reliance on fossil fuels contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating climate change and its devastating impacts.
Solutions and Strategies for Addressing Electricity Supply Challenges
The challenges faced by developing regions are complex, but there are numerous solutions and strategies that can be employed to improve electricity access and foster sustainable development.
-
Investing in Grid Infrastructure and Renewable Energy:
- Grid Expansion: Upgrading and expanding electricity grids to reach underserved populations is critical for improving reliability and ensuring widespread access to electricity. This involves investing in transmission lines, distribution networks, and other essential infrastructure.
- Renewable Energy Adoption: Investing in renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower is essential for providing clean, sustainable, and affordable electricity solutions. This involves promoting research and development, providing financial incentives, and fostering supportive policy frameworks.
-
Promoting Public-Private Partnerships:
- Collaboration between governments and private companies can leverage expertise, mobilize capital, and accelerate electrification initiatives. Public-private partnerships can foster innovation, improve project efficiency, and create sustainable business models for electricity provision.
-
Developing Robust Policy Frameworks:
- Clear and effective energy policies are essential for creating an enabling environment for private sector investment, promoting renewable energy development, and ensuring sustainable electricity access. This involves implementing transparent regulations, providing incentives for renewable energy adoption, and fostering an environment conducive to innovation.
-
Supporting Education and Training:
- Investing in education and training programs is crucial for developing a skilled workforce capable of operating, maintaining, and managing electricity infrastructure. This involves strengthening vocational training programs, providing scholarships for specialized education, and creating opportunities for workforce development in the electricity sector.
Case Studies and Success Stories of Electrification Initiatives
Numerous examples highlight the successful implementation of electrification initiatives in developing regions.
-
The “Solar Home Systems” program in Bangladesh has empowered millions of rural households with affordable solar energy. This project showcases the potential of renewable energy technologies to provide clean and sustainable electricity access in remote areas.
-
The “Off-Grid Renewable Energy for Rural Development” project in India has helped to improve access to electricity in rural communities through the deployment of microgrids powered by solar and wind energy. This program demonstrates the effectiveness of combining decentralized energy solutions with community involvement.
-
The “Power Africa” initiative launched by the US government aims to increase access to electricity in sub-Saharan Africa. This multi-stakeholder effort involves partnerships with governments, private companies, and development organizations to promote investment in power generation, transmission, and distribution infrastructure.
These case studies demonstrate that effective electrification initiatives require a combination of factors, including strong government support, private sector investment, community involvement, and the adoption of innovative technologies.
Future Trends and Opportunities in Electrification
The future of electrification in developing regions is marked by exciting opportunities and emerging trends.
-
Off-grid Solutions: The growing popularity of off-grid solutions powered by renewable energy sources like solar and wind offers a promising avenue for providing electricity access in areas lacking grid infrastructure. Microgrids and decentralized energy systems are becoming increasingly viable options, particularly for rural communities and remote locations.
-
Energy Storage: Advances in energy storage technologies are enabling the more efficient integration of renewable energy sources into electricity grids. Battery storage systems can store excess energy generated from solar and wind power, providing a reliable source of power during periods of low sunlight or wind.
-
Smart Grids: The implementation of smart grid technologies offers significant benefits for electricity access and reliability. Smart grids enable better monitoring of electricity flows, enhance grid management, and facilitate the integration of distributed energy sources, ultimately contributing to more efficient and sustainable electricity systems.
Conclusion
Electricity access is fundamental to economic growth, social progress, and sustainable development in developing regions. While significant challenges exist, there are numerous solutions and strategies that can be implemented to overcome these barriers.
Investing in grid infrastructure, promoting renewable energy adoption, fostering public-private partnerships, developing robust policy frameworks, and supporting education and training are all crucial components of a successful electrification strategy.
By embracing innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to sustainable solutions, developing regions can unlock the transformative power of electricity and build a brighter future for all.
For more information on electricity and water solutions, visit our website at: **https://diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn
Please feel free to leave your thoughts, share this information with others, or explore more resources on our website!
FAQs about Electricity Supply Challenges in Developing Regions
What are the main reasons for limited electricity access in developing regions?
Developing regions face a multitude of challenges in providing reliable and sufficient electricity supply. Some of the primary reasons include:
- Limited grid infrastructure: In many developing regions, particularly in rural areas, the electricity grid infrastructure is limited and underdeveloped, making it difficult to reach remote populations.
- Outdated technology: Many developing countries rely on aging and inefficient power generation systems, often heavily reliant on fossil fuels.
- Lack of investment in renewable energy: Despite the potential of renewable energy sources, investment remains limited due to financial constraints, technological complexities, and inadequate policy support.
- Economic and financial barriers: Poverty, high debt burdens, and limited access to capital can make it difficult to secure financing for large-scale electrification projects.
- Political and social factors: Political instability, corruption, and a lack of government support and effective policy frameworks can hinder electrification efforts.
What are some of the consequences of limited electricity access in developing regions?
Limited electricity access has severe consequences, including:
- Hindered economic growth: Businesses struggling with unreliable power supply may struggle to grow and create jobs.
- Health and education challenges: Healthcare facilities without reliable power face disruptions, impacting the delivery of essential services. Schools with limited electricity access may struggle to provide quality education.
- Environmental concerns: Reliance on fossil fuels for power generation leads to air pollution, contributing to health problems and exacerbating climate change.
What are some potential solutions to address electricity supply challenges in developing regions?
Addressing electricity supply challenges in developing regions requires a multi-pronged approach:
- Investing in grid infrastructure and renewable energy: Expanding and upgrading electricity grids to reach underserved populations and investing in renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower are crucial.
- Promoting public-private partnerships: Collaborations between governments and private companies can leverage expertise, mobilize capital, and accelerate electrification initiatives.
- Developing robust policy frameworks: Clear and effective energy policies are essential for creating an enabling environment for private sector investment, promoting renewable energy development, and ensuring sustainable electricity access.
- Supporting education and training: Investing in education and training programs is crucial for developing a skilled workforce capable of operating and maintaining electricity infrastructure.
How can developing countries leverage renewable energy to address electricity supply challenges?
Developing countries can leverage renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower to provide clean, sustainable, and affordable electricity solutions. These technologies offer several advantages:
- Sustainable and clean energy: Renewable energy sources are environmentally friendly and produce no greenhouse gas emissions, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change impacts.
- Cost-effective: Renewable energy technologies have become increasingly cost-competitive with traditional fossil fuel power plants, particularly in regions with abundant solar and wind resources.
- Decentralized solutions: Renewable energy sources can be deployed in decentralized systems, providing electricity to remote areas without the need for extensive grid infrastructure.
What role do international organizations play in addressing electricity supply challenges in developing regions?
International organizations like the World Bank, the International Finance Corporation (IFC), and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) play a crucial role in addressing electricity supply challenges in developing regions.
- Financing: These organizations provide funding for electrification projects, supporting infrastructure development and renewable energy initiatives.
- Technical Expertise: They provide technical assistance, capacity building, and knowledge sharing to help developing countries implement sustainable energy solutions.
- Policy Support: They work with governments to develop and implement effective policies that encourage private sector investment and promote renewable energy adoption.
Entities, Relations, and Semantic Triples
Entities:
- Developing Countries
- Electricity Access
- Power Plants
- Transmission Lines
- Renewable Energy Sources
- Energy Efficiency Programs
- Smart Grids
- International Organizations
- Private Companies
- Research Institutions
- Poverty
- Economic Growth
- Climate Change
- Technological Innovation
- International Cooperation
- Social Impact
- Human Development
- Electricity Infrastructure
- Energy Policy
Relations:
- Have
- Produce
- Transport
- Provide
- Reduce
- Improve
- Enable
- Guides
- Increased By
- Contributed To By
- Drives
- Promotes
- Enhanced By
- Limited By
- Face
- Crucial For
- Required For
- Invest
- Develop
Semantic Triples:
- Subject: Developing Countries | Predicate: Have | Object: Limited Electricity Access
- Subject: Power Plants | Predicate: Produce | Object: Electricity
- Subject: Transmission Lines | Predicate: Transport | Object: Electricity
- Subject: Renewable Energy Sources | Predicate: Provide | Object: Sustainable Energy
- Subject: Energy Efficiency Programs | Predicate: Reduce | Object: Energy Consumption
- Subject: Smart Grids | Predicate: Improve | Object: Electricity Reliability
- Subject: International Organizations | Predicate: Provide | Object: Financial Support
- Subject: Private Companies | Predicate: Invest | Object: Electricity Infrastructure
- Subject: Research Institutions | Predicate: Develop | Object: New Energy Technologies
- Subject: Electricity Infrastructure | Predicate: Enables | Object: Economic Growth
- Subject: Energy Policy | Predicate: Guides | Object: Electricity Development
- Subject: Poverty | Predicate: Increased By | Object: Lack of Electricity Access
- Subject: Climate Change | Predicate: Contributed To By | Object: Fossil Fuel Reliance
- Subject: Technological Innovation | Predicate: Drives | Object: Renewable Energy Adoption
- Subject: International Cooperation | Predicate: Promotes | Object: Sustainable Energy Solutions
- Subject: Social Impact | Predicate: Enhanced By | Object: Improved Electricity Access
- Subject: Human Development | Predicate: Limited By | Object: Lack of Electricity Access
- Subject: Rural Areas | Predicate: Face | Object: Greater Challenges in Electricity Access
- Subject: Energy Access | Predicate: Crucial For | Object: Sustainable Development
- Subject: Grid Expansion | Predicate: Required For | Object: Reliable Electricity Supply
EAVs (Entity – Attribute – Value):
- Entity: Developing Countries | Attribute: GDP Per Capita | Value: Low
- Entity: Developing Countries | Attribute: Electricity Access Rate | Value: Below 50%
- Entity: Power Plants | Attribute: Technology | Value: Coal-fired, Diesel, Hydropower
- Entity: Transmission Lines | Attribute: Length | Value: Limited
- Entity: Renewable Energy Sources | Attribute: Potential | Value: High
- Entity: Rural Areas | Attribute: Electricity Access Rate | Value: Lower than Urban Areas
- Entity: Energy Poverty | Attribute: Impact | Value: Hinders Economic Development
- Entity: Energy Efficiency Programs | Attribute: Benefits | Value: Lower Energy Consumption
- Entity: Smart Grids | Attribute: Advantages | Value: Improved Reliability, Reduced Costs
- Entity: International Organizations | Attribute: Role | Value: Financing, Policy Support
- Entity: Private Companies | Attribute: Role | Value: Investment, Technology Development
- Entity: Research Institutions | Attribute: Role | Value: Innovation, Technology Development
- Entity: Electricity Infrastructure | Attribute: State | Value: Aging, Underdeveloped
- Entity: Energy Policy | Attribute: Focus | Value: Increasing Access, Sustainability
- Entity: Economic Growth | Attribute: Impact | Value: Hindered by Limited Electricity Access
- Entity: Climate Change | Attribute: Impact | Value: Increased Reliance on Fossil Fuels
- Entity: Technological Innovation | Attribute: Role | Value: Developing New Energy Solutions
- Entity: International Cooperation | Attribute: Importance | Value: Sharing Knowledge, Resources
- Entity: Social Impact | Attribute: Benefits | Value: Improved Quality of Life, Education, Healthcare
- Entity: Human Development | Attribute: Impact | Value: Enhanced by Increased Electricity Access
