Electricity and Water News
National Electricity Outage Response Protocols: A Guide for Preparedness & Recovery
National Electricity Outage Response Protocols: A Guide for Preparedness & Recovery. In today’s article, diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding National Electricity Outage Response Protocols: A Guide for Preparedness and Recovery
Electricity is the lifeblood of our modern world. It powers our homes, businesses, and essential services. But what happens when the lights go out? What happens when a national electricity outage strikes, plunging entire communities into darkness? This is where response protocols become essential, providing a framework for preparedness and recovery.
A national electricity outage can be caused by a variety of factors, from natural disasters like hurricanes and earthquakes to man-made incidents like cyberattacks and equipment failures. These outages can have a profound impact on our daily lives, disrupting communication, transportation, and access to critical services like healthcare and emergency response.
The ability to respond effectively to a national electricity outage depends on a coordinated effort involving various stakeholders, including government agencies, utility companies, and the private sector. These entities must work together to ensure swift recovery, minimize disruption, and protect public safety.
Types of National Electricity Outages:
There are two primary types of national electricity outages: planned and unplanned.
-
Planned Outages: These are scheduled interruptions of power, often for maintenance, upgrades, or repairs to the national grid. Planned outages are usually communicated in advance to the public, allowing for preparation and minimizing inconvenience.
-
Unplanned Outages: These are unexpected disruptions to power supply, often caused by unforeseen events like natural disasters, equipment failures, or cyberattacks. Unplanned outages pose unique challenges, requiring swift and coordinated response efforts to restore power and minimize damage.
Key Stakeholders in Outage Response:
The success of any national electricity outage response depends on the coordinated efforts of several key stakeholders.
-
Government Agencies: Federal, state, and local government agencies play critical roles in coordinating response efforts. Agencies like the Department of Energy and FEMA (Federal Emergency Management Agency) are responsible for developing national strategies, providing guidance, and coordinating resources during outages.
-
Utility Companies: Electricity providers are at the forefront of outage response. They are responsible for identifying the cause of the outage, isolating the affected area, repairing damaged infrastructure, and restoring power as quickly and safely as possible. They also communicate with customers, providing updates on the status of the outage and estimated restoration times.
-
Private Sector: Other private entities, including critical infrastructure operators, telecommunications companies, and financial institutions, also play vital roles in outage response. They may be responsible for providing essential services, maintaining communication networks, and supporting recovery efforts.
Essential Elements of Effective Response Protocols:
Effective national electricity outage response protocols must include several essential elements:
-
Situational Awareness and Communication: Real-time information is crucial for effective response. Monitoring systems and communication channels must be in place to gather information about the outage, assess the impact, and disseminate updates to stakeholders. Coordinated communication across government agencies, utility companies, and the private sector is vital for efficient response.
-
Resource Allocation and Deployment: Responding to a national electricity outage requires the mobilization of resources, including personnel, equipment, and supplies. Pre-planning and clear protocols for resource allocation are crucial to ensure the efficient deployment of resources where they are most needed. Challenges arise when coordinating resource allocation across multiple agencies and organizations.
-
Incident Management and Coordination: Effective national electricity outage response requires a centralized command and control structure to manage the overall effort. Different incident management models, such as the Incident Command System (ICS), are used to ensure efficient communication, decision-making, and resource coordination.
-
Public Information and Outreach: Effective communication with the public is vital during a national electricity outage. Government agencies, utility companies, and other stakeholders must communicate timely, accurate, and consistent information to the public, providing updates on the status of the outage, safety tips, and estimated restoration timelines. This communication can be achieved through websites, social media, emergency alerts, and other channels.
Real-World Applications: Case Studies and Best Practices
The effectiveness of national electricity outage response protocols can be assessed through case studies of previous outages.
-
Successful Response Protocols: By analyzing successful responses, we can identify key factors that contributed to their effectiveness. These factors may include strong coordination among stakeholders, efficient communication strategies, robust resource mobilization, and clear incident management procedures.
-
Areas for Improvement: Case studies can also highlight areas where response protocols can be enhanced. These might include identifying weaknesses in coordination, communication, or resource allocation, or exploring the implementation of new technologies or strategies.
Preparing for the Future: Trends and Challenges in National Electricity Outage Response
National electricity outage response protocols must be constantly evolving to address emerging technologies and challenges.
-
Emerging Technologies: New technologies are playing an increasingly important role in outage response. Smart grids, microgrids, and energy storage are emerging as key solutions for enhancing grid resilience and improving outage recovery times.
-
Future Challenges: Climate change, cyber threats, and aging infrastructure pose significant challenges to the electric grid, increasing the likelihood and severity of outages. Response protocols must be adapted to address these challenges and ensure that the grid is resilient to future disruptions.
FAQs About National Electricity Outage Response Protocols
What are the main causes of national electricity outages?
National electricity outages can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
-
Natural Disasters: Hurricanes, earthquakes, tornadoes, floods, and other extreme weather events can damage power lines, transformers, and other critical infrastructure, leading to outages.
-
Equipment Failures: Equipment failures, such as transformer failures, can also cause outages. These failures may be due to age, wear and tear, or manufacturing defects.
-
Cyberattacks: Cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure, including the power grid, can disrupt operations and lead to outages.
-
Human Error: Human error, such as accidents or incorrect operation of equipment, can also contribute to outages.
What are the responsibilities of utility companies during a national electricity outage?
Utility companies play a critical role in outage response. Their responsibilities include:
-
Fault Isolation and Repair: Identifying the cause of the outage, isolating the affected area, and repairing damaged infrastructure.
-
Restoration of Power: Restoring power to customers as quickly and safely as possible.
-
Communication with Customers: Providing updates on the status of the outage, estimated restoration times, and safety tips.
What are the roles of government agencies in national electricity outage response?
Government agencies at all levels play vital roles in coordinating and supporting outage response efforts. Their roles include:
-
Developing National Strategies: Developing and implementing national-level policies and strategies to enhance grid resilience and improve outage response.
-
Providing Guidance: Providing guidance and support to utility companies, first responders, and other stakeholders involved in outage response.
-
Coordinating Resources: Allocating and coordinating the use of resources, such as personnel, equipment, and funding, to support outage response.
-
Public Information: Providing timely and accurate information to the public about the status of the outage and safety recommendations.
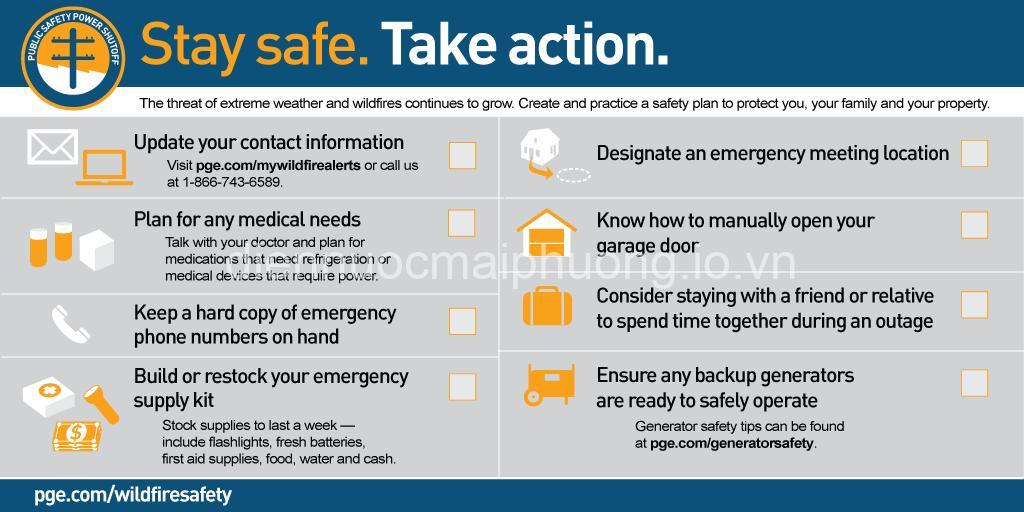
What can individuals do to prepare for a national electricity outage?
Individuals can take several steps to prepare for a potential outage:
-
Develop an Emergency Plan: Create a plan that outlines how you will communicate with family members, access essential supplies, and stay safe during an outage.
-
Assemble an Emergency Kit: Gather supplies like food, water, flashlights, batteries, first-aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
-
Identify Alternative Power Sources: Consider options for backup power, such as a generator, solar panels, or battery-powered devices.
What are some best practices for effective national electricity outage response protocols?
Some best practices for effective national electricity outage response protocols include:
-
Pre-planning and Coordination: Develop comprehensive plans and protocols that outline roles and responsibilities, communication procedures, and resource allocation strategies.
-
Robust Communication Systems: Establish secure and reliable communication systems to ensure effective information sharing among stakeholders.
-
Effective Incident Management: Utilize a centralized command and control structure to coordinate response efforts and make informed decisions.
-
Public Education and Outreach: Educate the public about potential outages, safety measures, and the importance of preparedness.
-
Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update response protocols based on lessons learned from past events and advancements in technology.
Conclusion
As an electrical and plumbing expert, I believe it’s crucial to be informed about national electricity outage response protocols. Being prepared can mean the difference between inconvenience and disaster. I encourage you to learn more about these protocols and to share this information with your family, friends, and community. To further enhance your understanding of electrical and water systems, I invite you to visit my website, diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn, and explore our comprehensive selection of high-quality products and resources. Together, we can empower ourselves and our communities to navigate the challenges of power outages and ensure a brighter future.
Semantic Keywords:
- National Electricity Outage
- Response Protocol
- Power Failure
- Emergency Preparedness
- Disaster Response
- Critical Infrastructure
- Resilience
- Public Safety
- Energy Security
EAV (Entity – Attribute – Value):
- National Electricity Outage – Duration – Hours, Days, Weeks
- National Electricity Outage – Cause – Natural Disaster, Cyberattack, Equipment Failure
- Government Agency – Role – Coordination, Resource Allocation, Public Information
- Utility Company – Responsibility – Restoration of Power, Communication with Customers, Fault Isolation
- Response Protocol – Stage – Assessment, Recovery, Mitigation
- Communication Strategy – Channel – Website, Social Media, Emergency Alerts
- Resource – Type – Personnel, Equipment, Supplies
- Incident Management – Model – Incident Command System (ICS), Unified Command
- Public Information – Content – Outage Status, Safety Tips, Restoration Timeline
- Case Study – Location – United States, Europe, Asia
- Best Practice – Element – Pre-planning, Coordination, Communication
- National Electricity Outage – Impact – Economy, Society, National Security
- Response Protocol – Effectiveness – Time to Restoration, Number of Affected Customers
- Government Agency – Involvement – Federal, State, Local
- Utility Company – Size – Small, Medium, Large
- Response Protocol – Development – Stakeholders, Experts, Government Agencies
- Communication Strategy – Effectiveness – Reach, Accuracy, Timeliness
- Resource – Availability – Limited, Abundant, Insufficient
- Incident Management – Challenges – Coordination, Communication, Resource Allocation
- Public Information – Success – Public Trust, Awareness, Compliance
ERE (Entity, Relation, Entity):
- Government Agency – Coordinates – Response Protocol
- Utility Company – Provides – Power Restoration
- Response Protocol – Includes – Communication Strategy
- Communication Strategy – Uses – Emergency Alerts
- Resource – Is Allocated By – Government Agency
- Incident Management – Utilizes – Incident Command System
- Public Information – Targets – Affected Public
- Case Study – Demonstrates – Best Practice
- National Electricity Outage – Impacts – Critical Infrastructure
- Response Protocol – Depends On – Stakeholder Collaboration
- Electricity Outage – Is Caused By – Natural Disaster
- Government Agency – Implements – Emergency Measures
- Utility Company – Operates – Power Grid
- Response Protocol – Defines – Roles and Responsibilities
- Communication Strategy – Facilitates – Information Sharing
- Resource – Enables – Outage Recovery
- Incident Management – Supports – Coordinated Response
- Public Information – Builds – Public Trust
- Case Study – Highlights – Lessons Learned
- Best Practice – Improves – Response Effectiveness
Semantic Triples (Subject, Predicate, Object):
- National Electricity Outage – has Cause – Natural Disaster
- Government Agency – has Role – Coordinating Response
- Utility Company – has Responsibility – Power Restoration
- Response Protocol – includes – Communication Strategy
- Communication Strategy – uses – Emergency Alerts
- Resource – is allocated by – Government Agency
- Incident Management – utilizes – Incident Command System
- Public Information – targets – Affected Public
- Case Study – demonstrates – Best Practice
- National Electricity Outage – impacts – Critical Infrastructure
- Response Protocol – depends on – Stakeholder Collaboration
- Electricity Outage – is caused by – Cyberattack
- Government Agency – implements – Emergency Measures
- Utility Company – operates – Power Grid
- Response Protocol – defines – Roles and Responsibilities
- Communication Strategy – facilitates – Information Sharing
- Resource – enables – Outage Recovery
- Incident Management – supports – Coordinated Response
- Public Information – builds – Public Trust
- Best Practice – improves – Response Effectiveness
