Electricity and Water News
National Grid Stability: Peak Demand & Power Outages Explained
National Grid Stability: Peak Demand & Power Outages Explained. In today’s article, diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding Peak Demand and its Impact on Grid Stability
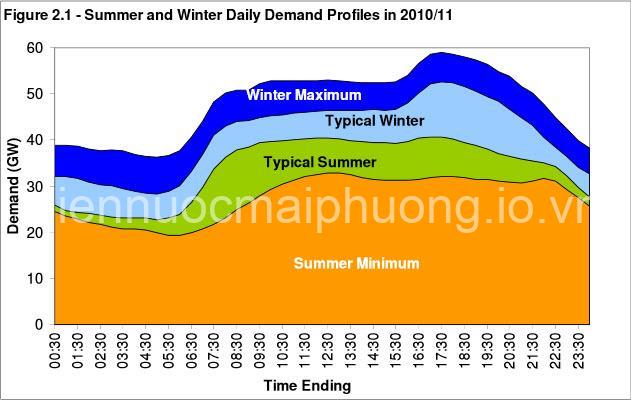
A stable electricity grid is the backbone of modern society, powering our homes, businesses, and essential services. But this delicate system faces constant pressure, particularly during peak demand periods. Peak demand refers to the highest point of electricity consumption within a specific timeframe, often occurring during hot summer days or cold winter nights when everyone uses more energy for cooling or heating.
Think about it: when temperatures soar and everyone turns on their air conditioners, the demand for electricity skyrockets. This strain on the grid can lead to various problems, including power outages and voltage fluctuations. Power outages can disrupt businesses, halt production, and leave homes in darkness. Voltage fluctuations, on the other hand, can damage sensitive electronic equipment.
Several factors contribute to peak demand, including:
- Seasonality: During summer, the use of air conditioners significantly increases the demand for electricity. Similarly, in winter, heating systems and holiday lighting put extra pressure on the grid.
- Time of Day: Evening hours typically see a surge in electricity consumption as people return home from work and turn on lights, appliances, and entertainment systems.
- Economic Activity: Industrial production and commercial activity contribute significantly to peak demand, especially during periods of economic growth or specific manufacturing cycles.
- Special Events: Major sporting events, concerts, and holidays can cause sudden surges in demand as people gather and use more electricity for lighting, entertainment, and food preparation.
These increased demands can cause the grid to become overloaded, potentially leading to power outages. The consequences of an unstable grid during peak demand extend beyond mere inconvenience; they can have serious economic and social implications.
Strategies for Maintaining Grid Stability During Peak Demand
Fortunately, there are various strategies that can be implemented to prevent grid overload and ensure a stable electricity supply during peak demand periods. These strategies can be broadly categorized into demand response and supply side solutions.
Demand Response: Managing Consumption
The idea behind demand response is to manage electricity consumption by adjusting usage patterns during peak demand hours. This involves incentivizing consumers to reduce their energy usage during high-demand periods. Several methods are used for demand response, including:
- Demand Side Management Programs: Utility companies often offer programs like time-of-use pricing to encourage consumers to shift their energy consumption to off-peak hours. These programs typically charge higher rates during peak hours and lower rates during off-peak hours.
- Smart Grids: Smart grids leverage communication technologies to monitor electricity usage in real-time and adjust demand accordingly. They can also automate processes like load shedding, where power is temporarily cut off to certain areas to reduce overall demand.
- Consumer Participation: Encouraging individual efforts to reduce energy consumption during peak hours is crucial. Consumers can contribute by using energy-efficient appliances, turning off lights when not in use, and adjusting thermostats to reduce heating or cooling demands.
Supply Side Solutions: Boosting Generation
While managing demand is essential, increasing electricity generation during peak hours is also critical. This involves exploring various supply side solutions to ensure sufficient power supply:
- Peak Power Plants: Peak power plants are designed to provide additional electricity during periods of high demand. These plants are typically fueled by natural gas and can be quickly ramped up and down as needed.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind into the grid can help reduce reliance on traditional power plants during peak demand. However, the intermittency of these sources, meaning their output is dependent on weather conditions, poses challenges.
- Energy Storage: Energy storage technologies play a vital role in grid stability. By storing energy generated during off-peak hours, batteries and other storage systems can release it when demand is high, ensuring a steady supply.
Grid Modernization: Updating Infrastructure
A key aspect of improving grid stability is grid modernization. This involves updating and upgrading existing infrastructure to make it more resilient and adaptable to changing demand patterns. Here are some critical aspects of grid modernization:
- Advanced Grid Technologies: Smart grids leverage advanced sensors, communication networks, and data analytics to monitor grid performance in real-time, enabling proactive adjustments and minimizing outages.
- Grid Automation: AI and automation play a critical role in grid modernization. They enable automatic adjustments to grid operations based on real-time data, allowing for faster responses to demand fluctuations.
- Interconnections and Regional Collaboration: Sharing resources and managing load across different regions can effectively balance supply and demand during peak periods.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
The strategies outlined above are being implemented globally, with several success stories demonstrating their effectiveness.
- Case Study 1: In California, time-of-use pricing has been instrumental in shifting energy consumption to off-peak hours, reducing strain on the grid during peak demand periods.
- Case Study 2: Germany has successfully integrated renewable energy sources like wind and solar power into its grid, demonstrating that clean energy can contribute to peak demand management.
However, challenges still exist, including the need to balance affordability with reliability. Integrating new technologies like energy storage requires significant investment, and ensuring affordability remains a key challenge.
Furthermore, addressing climate change is a critical aspect of grid stability. As extreme weather events become more frequent, the need for a resilient grid that can withstand these challenges grows increasingly urgent.
The Future of Grid Stability
The future of grid stability hinges on continued innovation and collaboration. Emerging technologies like advanced energy storage, grid-scale batteries, and smart grids will play a crucial role in ensuring a stable and reliable electricity supply.
To achieve this, it is essential for governments, utilities, technology companies, and consumers to work together to develop and implement sustainable solutions.
The future of our electricity grid is bright, with exciting advancements on the horizon. By embracing these innovations and collaborating to find solutions, we can ensure a reliable and resilient energy infrastructure for generations to come.
Conclusion
The information in this article can help you understand the complexities of grid stability and the factors affecting power outages during peak demand periods. It’s essential to be informed about these issues as it affects every aspect of our lives. For more information on electrical and plumbing solutions, visit diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn.
Please leave a comment below to share your thoughts or questions. You can also share this article with your friends and family to spread awareness about grid stability.
FAQs
What are the common causes of power outages during peak demand?
Power outages during peak demand can occur due to various factors, including:
- Overloading: When the demand for electricity exceeds the capacity of the grid, it can cause overloading and lead to a power outage.
- Equipment Failure: Faulty transformers, transmission lines, or other grid equipment can fail under heavy load, causing power outages.
- Extreme Weather: Storms, hurricanes, and extreme temperatures can damage grid infrastructure and cause power disruptions.
How can I reduce my electricity consumption during peak demand?
You can contribute to grid stability by reducing your energy consumption during peak hours. Some ways to do this include:
- Use energy-efficient appliances: Upgrade to energy-efficient appliances that consume less energy.
- Turn off lights and appliances when not in use: Practice this habit to reduce your overall energy consumption.
- Adjust thermostats: Set your thermostat to a comfortable temperature during peak demand hours to reduce heating or cooling needs.
- Use timers and smart plugs: Utilize timers and smart plugs to automate the turning off of lights and appliances when not in use.
What is the role of renewable energy in grid stability?
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind can contribute to grid stability by reducing dependence on traditional power plants. However, their intermittency, meaning their output fluctuates based on weather conditions, poses challenges. Energy storage technologies are crucial for integrating renewable energy sources into the grid and ensuring a steady supply during peak demand.
What are the benefits of grid modernization?
Grid modernization involves upgrading existing infrastructure to make it more resilient and adaptable to changing demands. The benefits include:
- Improved reliability: A modernized grid is less susceptible to outages and disruptions.
- Enhanced efficiency: Advanced technologies enable better grid management and reduce energy losses.
- Increased capacity: A modernized grid can handle higher demand and accommodate the integration of renewable energy sources.
- Enhanced security: Modernization strengthens grid security against cyber threats and physical attacks.
What can governments and utilities do to promote grid stability?
Governments and utilities play a crucial role in promoting grid stability by implementing policies and investing in infrastructure. Some actions they can take include:
- Incentivize energy efficiency: Offer rebates and tax incentives for consumers to purchase energy-efficient appliances.
- Promote renewable energy development: Support the growth of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
- Invest in grid modernization: Fund projects to upgrade grid infrastructure and implement smart grid technologies.
- Develop comprehensive demand response programs: Offer programs that encourage consumers to shift their energy consumption to off-peak hours.
