Electricity and Water News
Water Scarcity Solutions in Growing Cities: Conservation & Innovation
Water Scarcity Solutions in Growing Cities: Conservation & Innovation. In today’s article, diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn will explore with you in the most detailed and complete way. See now!
Understanding Water Scarcity in Rapidly Growing Cities
The world is experiencing a rapid pace of urbanization, with more and more people migrating to cities in search of opportunities. This population boom puts a strain on water resources, especially in areas already facing water scarcity. As cities grow, the demand for water increases exponentially, while natural water sources remain limited.
Urbanization itself has a significant impact on the availability of water. Concrete and asphalt surfaces replace natural landscapes, reducing the ability of the land to absorb rainwater. This leads to increased runoff, which can overwhelm drainage systems and contribute to flooding. Furthermore, urbanization often pollutes water sources, making them unsuitable for drinking or irrigation.
Climate change further exacerbates the challenges of water scarcity. Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns lead to more frequent droughts, reducing the amount of water available in rivers, lakes, and underground aquifers.
The consequences of water scarcity are far-reaching. Cities face challenges in providing adequate water for drinking, sanitation, and irrigation, which can lead to health problems, social unrest, and economic decline.
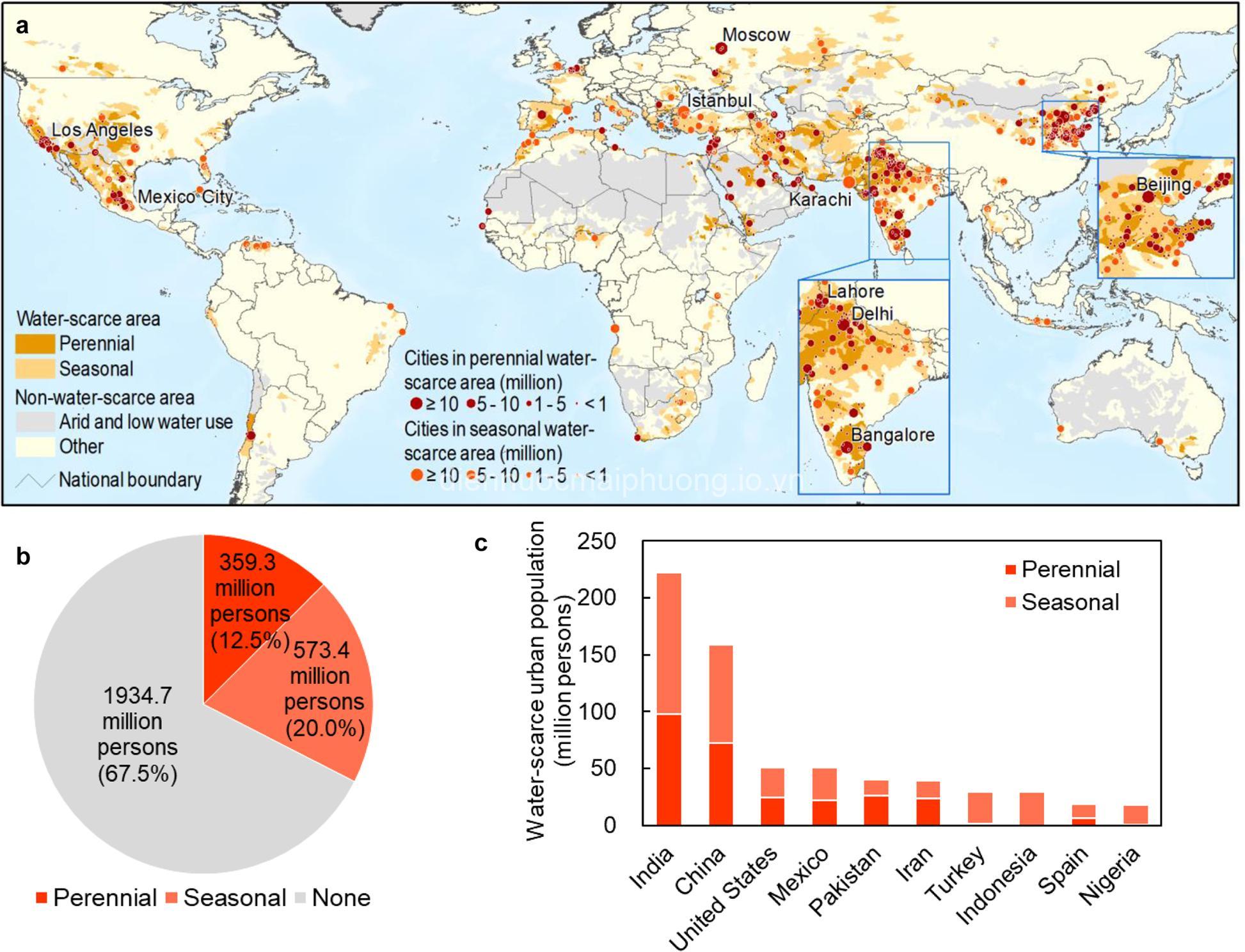
Conservation and Efficiency: The Cornerstones of Water Management
Conserving water and using it efficiently are crucial for managing water scarcity in growing cities. Here are some practical strategies to address the challenge:
- Water-efficient technologies play a key role in reducing water consumption. Installing low-flow showerheads, water-efficient toilets, and drip irrigation systems can significantly reduce water usage in homes, businesses, and public spaces.
- Smart water management uses sensors and data analytics to monitor water usage, detect leaks, and optimize water distribution. This technology enables cities to identify and address water waste, ensuring more efficient use of precious resources.
- Public awareness and behavioral change are essential components of water conservation. Educating citizens about the importance of water conservation and providing them with practical tips can encourage them to reduce their water usage.
- Pricing strategies can incentivize water conservation. Implementing tiered pricing systems that charge higher rates for excessive water usage can encourage residents and businesses to use water more responsibly.
Innovative Solutions: Rethinking Water Supply and Reuse
In addition to conservation, innovative solutions are needed to expand water supply and reuse existing water resources. Here are some key approaches:
- Water harvesting involves collecting rainwater and storing it for later use. This practice can be implemented in homes, businesses, and public spaces, reducing reliance on conventional water sources.
- Greywater treatment involves treating wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry machines to use for irrigation, cleaning, or other non-potable purposes. Greywater reuse can significantly reduce the demand for fresh water.
- Desalination technologies remove salt from seawater, providing a reliable source of drinking water. This technology is becoming increasingly important in coastal areas with limited freshwater sources.
- Wastewater treatment and reuse involves treating wastewater for non-potable purposes, such as irrigation or industrial uses. By reusing treated wastewater, cities can reduce their reliance on fresh water sources.
Sustainable Urban Planning: Designing Water-Resilient Cities
Urban planning plays a crucial role in ensuring a sustainable water future for cities. Here are some essential considerations:
- Green infrastructure includes features like green roofs, permeable paving, and urban green spaces. These features help to absorb rainwater, reduce runoff, and improve the city’s ability to handle storms.
- Integrated water management involves a holistic approach to water management that considers all aspects of water supply, treatment, and distribution. This approach ensures that water resources are managed effectively and efficiently.
- Urban agriculture and vertical farming can help reduce water demand. Growing food locally reduces the need for transporting produce from distant farms, which often requires significant water resources. Vertical farms, which grow crops in layers, can be particularly water-efficient.
Case Studies of Successful Water Scarcity Solutions
- Singapore: Singapore has implemented a comprehensive water management strategy, focusing on water conservation, desalination, and wastewater reuse. The country’s “Four National Taps” strategy emphasizes the use of four sources of water: local catchment water, imported water, desalination, and recycled water. This approach has made Singapore a model for water security in urban areas.
- Cape Town, South Africa: Cape Town faced a severe drought in 2018, leading to a “Day Zero” scenario where the city was on the verge of running out of water. The city responded with an aggressive water conservation campaign, reducing water usage by over 50%. Cape Town’s experience highlights the importance of proactive water management and public engagement in addressing water scarcity.
The Future of Water Security in Growing Cities
Moving forward, technological advancements and global collaboration are essential for ensuring water security in growing cities.
- Emerging technologies continue to improve water treatment, desalination, and water management practices. Advanced technologies like AI and machine learning are being used to optimize water distribution, predict water demand, and identify leaks.
- Global collaboration is essential for sharing best practices and knowledge. International cooperation can facilitate the transfer of technology and support the development of sustainable water management solutions in developing countries.
As cities grow and water resources become increasingly scarce, it is crucial to embrace a future-oriented approach to water management. By embracing conservation, innovation, and collaboration, we can secure a sustainable water future for our urban populations.
What are some of the most effective ways to conserve water in cities?
Water conservation is a multi-faceted approach that involves:
- Reducing water usage in homes, businesses, and public spaces through water-efficient appliances and fixtures.
- Implementing smart water management systems to detect leaks and optimize water distribution.
- Promoting public awareness and behavioral change through educational campaigns and incentives for water conservation.
- Developing water pricing strategies that encourage responsible water use.
What are the biggest challenges to implementing water scarcity solutions in cities?
Challenges include:
- Outdated infrastructure that can lead to leaks and waste.
- Lack of political will and funding to invest in water infrastructure improvements.
- Limited public awareness and engagement in water conservation practices.
- Social equity issues that may prevent equal access to water resources.
What is the role of technology in addressing water scarcity?
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing water management:
- Water treatment technologies provide clean and safe drinking water.
- Sensors and data analytics help monitor water usage, detect leaks, and optimize distribution.
- AI and machine learning can be used to predict water demand and optimize resource allocation.
How can cities plan for a more sustainable water future?
Sustainable water planning involves:
- Adopting a holistic water management approach that integrates water supply, treatment, and distribution.
- Prioritizing green infrastructure to increase water retention and infiltration.
- Promoting water conservation through education, incentives, and pricing strategies.
- Investing in water-efficient technologies to reduce water demand.
Conclusion
As cities continue to grow, addressing water scarcity will remain a top priority. By embracing conservation strategies, innovative technologies, and sustainable urban planning, we can ensure a water-secure future for our urban populations.
To learn more about water and electrical solutions, visit my website: https://diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn.
Jessica David Rodriguez, owner of diennuocmaiphuong.io.vn, is a leading expert in water and electrical solutions, committed to providing practical solutions for a sustainable future.
Don’t forget to leave a comment, share this article with your friends, and explore more informative content on my website!
Semantic Keywords:
- Urban Water Management
- Water Conservation
- Sustainable Cities
- Water Security
- Water Reuse
- Climate Change Adaptation
- Urban Planning
- Water Infrastructure
- Water Scarcity Solutions
EVAs:
- Entity: Water Scarcity | Attribute: Causes | Value: Urbanization, Population Growth, Climate Change
- Entity: City | Attribute: Population | Value: Rapidly Growing
- Entity: Desalination | Attribute: Technology | Value: Water Treatment, Water Supply
- Entity: Rainwater Harvesting | Attribute: Method | Value: Water Collection, Water Conservation
- Entity: Greywater | Attribute: Use | Value: Irrigation, Non-Potable Water
- Entity: Urban Planning | Attribute: Goal | Value: Water Conservation, Sustainable Development
- Entity: Smart City | Attribute: Feature | Value: Water Management, Data Analytics
- Entity: Water Infrastructure | Attribute: Condition | Value: Outdated, Inefficient
- Entity: Water Conservation | Attribute: Strategy | Value: Water Efficiency, Water Reuse
- Entity: Climate Change | Attribute: Impact | Value: Droughts, Water Scarcity
- Entity: Population Growth | Attribute: Effect | Value: Increased Water Demand, Urbanization
- Entity: Technology | Attribute: Role | Value: Water Treatment, Water Management
- Entity: Environment | Attribute: Impact | Value: Water Quality, Water Scarcity
- Entity: Water | Attribute: Resource | Value: Limited, Scarce
- Entity: Cities | Attribute: Type | Value: Rapidly Growing, Urban
- Entity: Urbanization | Attribute: Trend | Value: Population Shift, Growth
- Entity: Water Reuse | Attribute: Purpose | Value: Irrigation, Non-Potable Water
- Entity: Water Management | Attribute: Approach | Value: Sustainable, Efficient
- Entity: Water Efficiency | Attribute: Measure | Value: Appliances, Fixtures
- Entity: Sustainable Development | Attribute: Goal | Value: Environmental Protection, Social Equity
EREs:
- City (Has) Population
- Water (Is Used for) Irrigation
- Climate Change (Causes) Water Scarcity
- Urbanization (Leads to) Water Demand
- Desalination (Produces) Drinking Water
- Greywater (Can Be Used for) Non-Potable Water
- Technology (Improves) Water Management
- Sustainable Planning (Promotes) Water Conservation
- Water Infrastructure (Affects) Water Supply
- Water Scarcity (Impacts) Economic Development
- Water Reuse (Reduces) Water Demand
- Population Growth (Increases) Urbanization
- Environment (Provides) Water Resources
- Rainwater Harvesting (Collects) Water
- Water Management (Aims to) Water Security
- Water Efficiency (Saves) Water
- Smart Cities (Utilize) Technology
- Water Scarcity (Threatens) Cities
- Cities (Implement) Water Conservation
- Urban Planning (Considers) Water Management
Semantic Triples:
- Water Scarcity is a major challenge for rapidly growing cities.
- Urbanization leads to increased water demand.
- Climate change impacts water availability.
- Desalination technology can provide additional water sources.
- Rainwater harvesting conserves water resources.
- Greywater can be reused for non-potable purposes.
- Sustainable urban planning promotes water efficiency.
- Smart cities use technology for water management.
- Water conservation is essential for urban sustainability.
- Water infrastructure needs to be modernized.
- Water reuse reduces water demand.
- Population growth contributes to water scarcity.
- The environment provides water resources.
- Water scarcity impacts economic development.
- Cities implement water conservation strategies.
- Urban planning considers water management.
- Water security is a critical goal for urban areas.
- Technology plays a crucial role in addressing water scarcity.
- Water efficiency is a key aspect of water conservation.
- Sustainable development aims to protect water resources.
